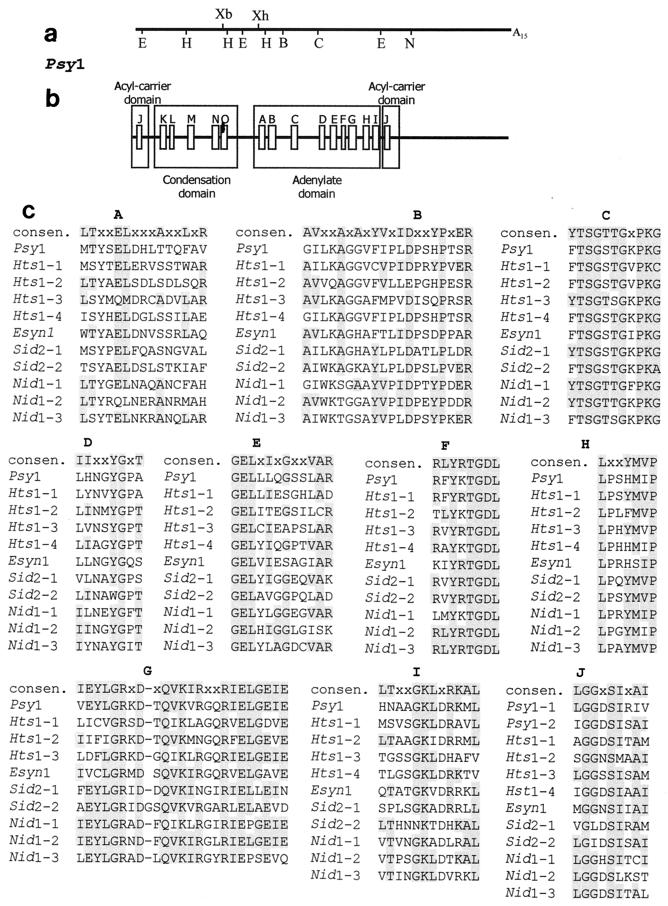
FIG. 1.
Restriction map and modular organization of Psy1 with regions of high sequence similarity to conserved adenylate domain motifs. (a) Restriction map of the 5,056-bp cloned cDNA of Psy1. Abbreviations: B, BamHI; C, ClaI; E, EcoRI; H, HindIII; S, SalI; N, NarI; Xb, XbaI; Xh, XhoI. (b) Regions of similarity to consensus sequence motifs of bacterial peptide synthetases (20). (c) Sequences in the motifs compared for the adenylate domains of Psy1 and other fungal peptide synthetases. Shading indicates sequence identity with the bacterial consensus sequence (consen.). Sequence comparisons were carried out with CLUSTALW (European Bioinformatics Institute [http://www2.ebi.ac.uk/clustalw]), and the entire adenylate domains and acyl carrier domains were used to preserve relative spacing between blocks. The genes used were the genes for ferrichrome siderophore synthetase (Sid2) from U. maydis (GenBank accession no. U62738), ACV synthetase (Nid1) from Aspergillus nidulans (GenBank accession no. X54853), HC toxin synthetase (Hts1) from C. carbonum (GenBank accession no. M98024), and enniatin synthetase (Esyn1) from Fusarium avenaceum (GenBank accession no. Z18755). Each adenylate domain/acyl carrier domain in a gene is numbered in the order of its appearance in the gene. However, Psy1 acyl carrier domain 2 (Psy1-2) is the acyl carrier domain located at the 5′ end of the cDNA and potentially is part of another incomplete synthetase unit. The relative organization of motifs is conserved in the adenylate domain; however, the organization of the condensation, adenylate, and acyl carrier domains is not the same for all genes.