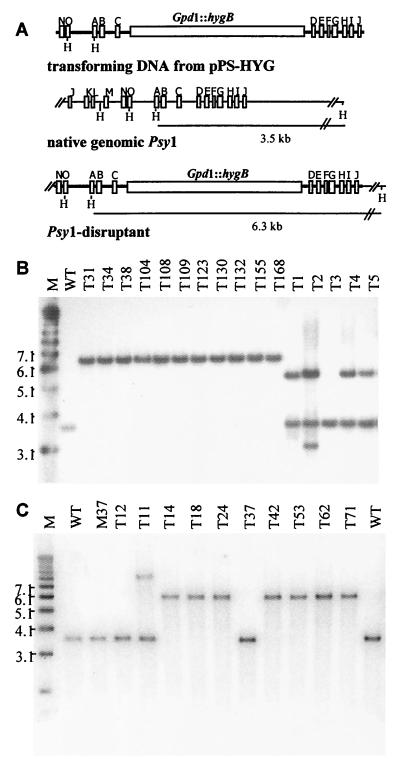
FIG. 2.
Disruption of the Psy1 gene in G20-4VIB (wild type) and non-gliotoxin-producing mutant G20-M37. (A) Gene disruption construct (pPS-HYGI) obtained by insertion of HygB (hygromycin phosphotransferase) expressed from the C. parasitica Gpd1 promoter (Gpd1::hygB) into the ClaI restriction site of the Psy1 cDNA insert in pPsy1. The positions of nucleotides corresponding to adenylate domain motifs A to O are indicated. PCR amplification with primers located at the termini of the Psy1 insert was used to produce a linear DNA fragment used for transformation to eliminate vector sequences. Insertion of the hygB cassette into native Psy1 resulted in a 2.8-kb increase in the size of the HindIII restriction fragment. (B) Southern blot analysis of HindIII-digested chromosomal DNA of T. virens wild-type strain G20-4VIB (lane WT) and transformants for detection of gene disruption events. Lane M contained molecular weight markers. (C) Southern blot analysis of HindIII-digested chromosomal DNA of T. virens wild-type strain G20-4VIB (lanes WT), gliotoxin mutant G20-M37 (lane M37), and G20-M37 transformants for detection of gene disruption events. Blots were probed with a 32P-labeled PCR fragment corresponding to the 3′ end of Psy1. Lane M contained molecular weight markers.