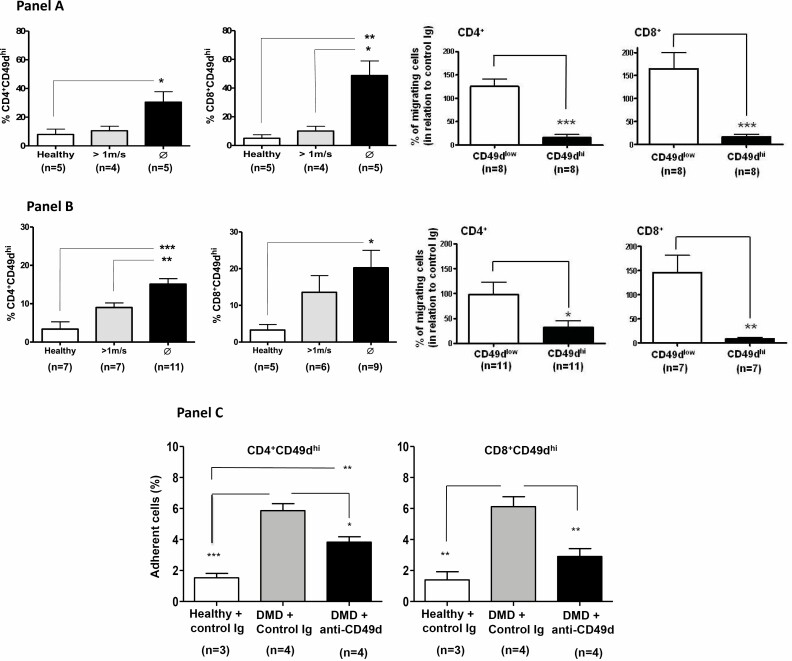
Figure 2.
Role of VLA-4 in migration and adhesion of T-cells from Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy patients: blockade by anti-VLA-4 monoclonal antibody. Panel A reveals that transendothelial migration of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells expressing high densities of CD49d from DMD patients and unable to walk migrate more than the patients able to walk (upper graphics). Importantly, migration of CD49dhi T cells is largely impaired in the presence of anti-VLA-4 antibody (bottom graphics). Similar enhancement of fibronectin-driven T cell migration is seen in panel B, which also shows that migration of CD49dhi T cell subsets is largely impaired in the presence of anti-VLA-4 antibody. Finally, panel C provides evidence showing that both CD4+CD49dhi and CD8+CD49dhi T cells subsets adhere more to cultured human myoblasts, and that such an increase is abrogated by anti-VLA-4 antibody, as compared to unrelated Immunoglobulin. Groups were statistically compared using the Kruskal–Wallis test followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. Modified from Pinto Mariz et al. 2015.