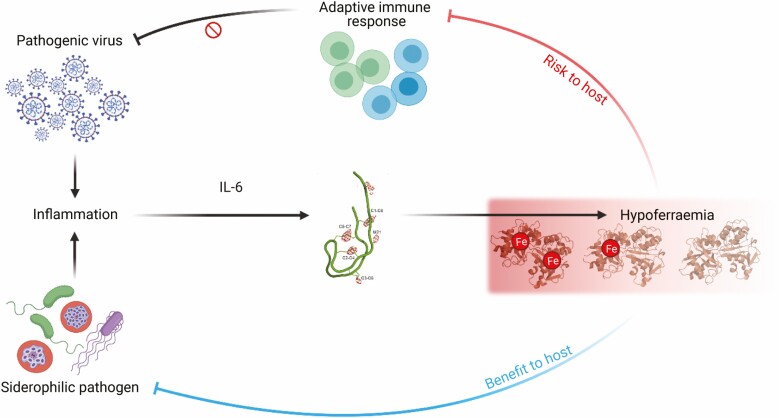
Figure 1.
Inflammation, often resulting from infection, induces hepcidin expression via IL-6, driving hypoferraemia. Hypoferraemia poses a trade-off to the host, limiting extracellular iron availability and protecting against siderophilic pathogens (e.g. Vibrio vulnificus), but also diverting iron away from the adaptive immune response, impairing control of pathogenic viruses (e.g. Influenza A virus infection).