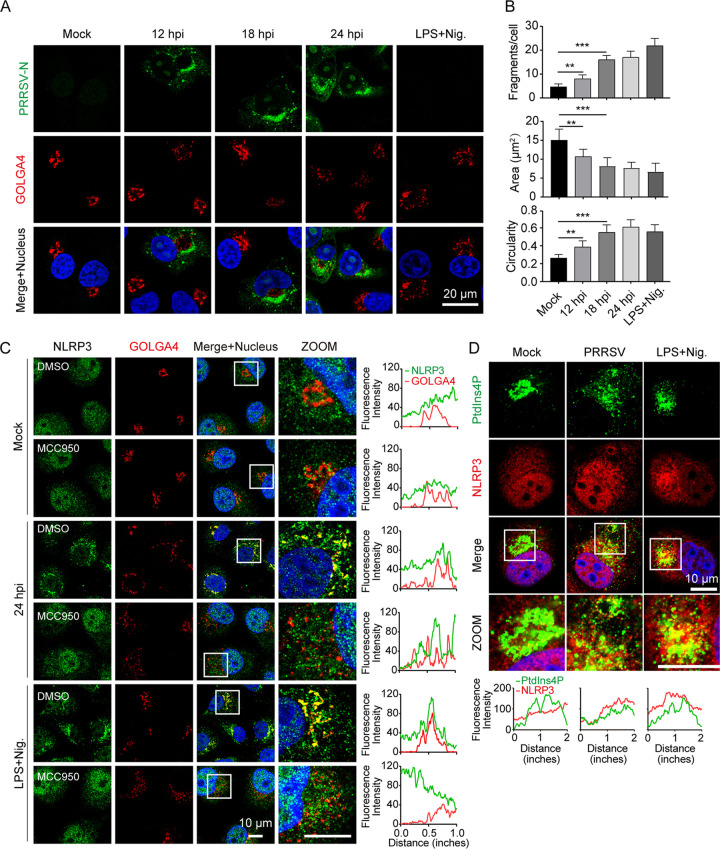
FIG 5.
Phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate (PtdIns4P) on dispersed trans-Golgi network mediates NLRP3 inflammasome activation during PRRSV infection. (A and B) Representative images showing that substantial trans-Golgi network (TGN) disassembly occurred in cells with PRRSV infection and nigericin stimulation, but not in mock-infected cells. Marc-145 cells were mock-infected or infected with PRRSV (MOI = 1) and fixed at the indicated time. As a positive control, cells were primed with LPS for 12 h, stimulated with nigericin (10 μM) for 45 min, and fixed. The trans-Golgi protein GOLGA4 (red) and PRRSV-N (green) were stained with specific antibodies. Nucleic acids were stained with DAPI (blue) (A). To quantify TGN disassembly, the numbers, areas, and circularities of TGN fragments for each cell were quantified from 200 randomly selected cells using ImageJ software for the data presented in panel A. Data represent the means ± SEM of ~200 cells for TGN markers from two independent experiments. (C) Immunofluorescence of cells labeled with NLRP3 and PRRSV-N antibodies. Marc-145 cell treatment was consistent with that shown in panel A, with or without MCC950. White boxes indicate zoomed areas. Colocalization quantifications were done using the Plot Profile plugin in ImageJ. (D) Marc-145 cells were treated as in panel A and stained with PtdIns4P and NLRP3 antibodies, followed by observation with confocal microscopy. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI. White boxes mark the zoomed areas shown in the bottom subpanels. Intracellular co-localization analysis of PtdIns4P and NLRP3 was done using the Plot Profile plugin in ImageJ.