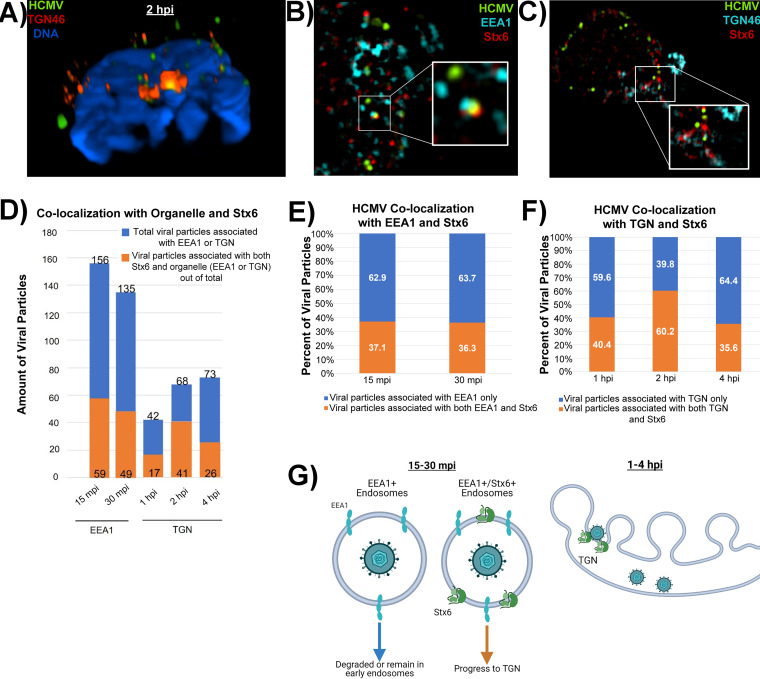
FIG 8.
HCMV particles that associate with both Stx6 and EEA1 early in infection fuse with the TGN. Primary human monocytes were synchronously infected with HCMV TB40/E (MOI = 10). The cells were fixed at 15 mpi, 30 mpi, 1 hpi, 2 hpi, and 4 hpi. The fixed cells were then stained with antibodies against HCMV (UL32-GFP), TGN (TGN46) or the early endosome (EEA1) (A), and Stx6 (B–E). High resolution images were acquired on a Nikon N-SIM E Super Resolution microscope system (100× objective) in single slices (z stacks) using the same laser settings. Representative images are shown. (A) Representative image of an infected monocyte at 2 hpi. Volumetric 3D reconstruction was performed on the image. The cross-section is shown. Yellow staining indicates colocalization (~0.1 μm distance). (B and C) Representative images of triple-stained infected monocytes. White boxes indicate areas within the image where triple colocalization occurs. (D) Total viral particles associated with the target organelle (~0.1 μm distance; blue bars) were manually quantified using the companion software to the microscope. Out of that population, the number of viral particles colocalized with both target organelle and Stx6 were quantified (orange bars). (E) The number of viral particles associated with organelle only or both organelle and Stx6 was calculated as percentages. (F) Model of likely biological events happening between virus-containing early endosomes and the TGN at the observed time points. N = 3.