Figure 2.
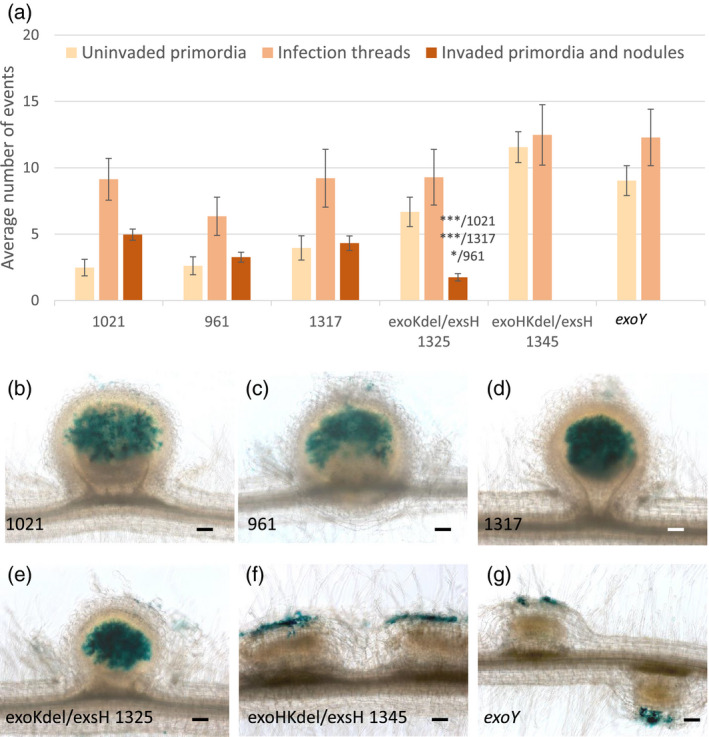
Infection and nodulation invasion phenotypes of the succinoglycan‐deficient exoY mutant and the exoHKdel/exsH‐1345 mutant on Medicago truncatula ssp. tricycla R108. Infection and nodule invasion phenotypes of M. truncatula WT R108 plants were scored 17 dpi following inoculation with six different Sinorhizobium meliloti strains; 1021, 961, exsH‐1317, exoKdel/exsH‐1325, exoHKdel/exsH‐1345 and exoY. The first three of these strains correspond to the unmodified WT strain (1021), a modified WT strain (961), which serves as a control for the expression of exoLAMON genes from a heterologous promoter, and exsH‐1317, which is identical to 961 except it lacks the exsH‐encoded glycanase. All three strains display an identical symbiotic phenotype. The double‐glycanase exoKdel/exsH‐1325 mutant (deficient for both the exoK and exsH glycanases) makes only HMW succinoglycan. The exoHKdel/exsH‐1345 mutant is isogenic to exoKdel/exsH‐1325, except that 1345 is missing the exoH succinyltransferase, and thus makes non‐succinylated HMW succinoglycan. exoY is completely deficient for production of succinoglycan.
(a) Quantification of uninvaded nodule primordia, infection threads, and invaded nodule primordia and nodules. Data are the averages of two independent experiments, n = 28 for each strain. Error bars = SEM. Statistically significant differences in invaded primordia and nodules between exoKdel/exsH‐1325 and other strains are indicated. *P < 0.05; ***P < 0.001.
(b–g) Photographs illustrating these infection phenotypes, all inoculated strains carrying a constitutive hemA‐lacZ reporter gene fusion (pXLGD4) for visualization of bacteria in blue. Fully invaded nodules were seen with 1021, 961, exsH‐1317 and exoKdelexsH‐1325 (b–e, respectively), while only uninvaded nodule primordia were observed with exoHKdel/exsH‐1345 and exoY (f and g, respectively). In these latter two cases, rhizobia appear restricted to the epidermis, but apparently continue to multiply in these unsuccessful infection compartments, resulting in excessively large root hair microcolonies. Scale bars: 100 µm.
