Figure 6.
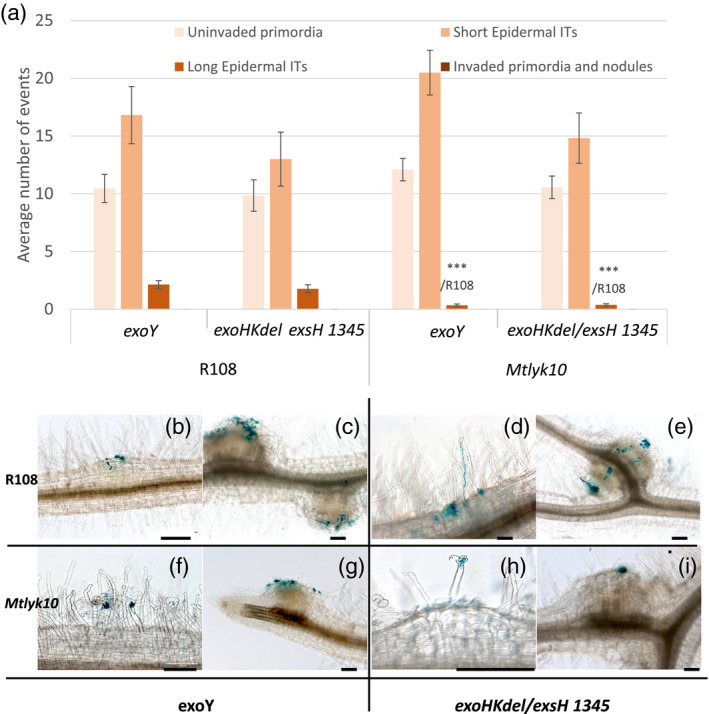
Infection and nodulation invasion phenotypes of the Sinorhizobium meliloti succinoglycan‐deficient exoY mutant and the exoHKdel/exsH‐1345 succinyltransferase mutant on M. truncatula lyk10 mutant plants. Infection and nodulation invasion phenotypes of M. truncatula Mtlyk10 mutant and R108 WT plants were scored 21 dpi following inoculation with the S. meliloti succinoglycan‐deficient exoY mutant or the S. meliloti exoHKdel/exsH‐1345 mutant, which makes non‐succinylated HMW succinoglycan.
(a) Quantification of uninvaded nodule primordia, and short and long epidermal infection threads. No invaded nodule primordia or invaded nodules were seen. Data are the averages of two independent experiments, n = 40 for each genotype/strain combination. Error bars = SEM. Statistically significant differences are indicated as ***/R108 to indicate that the comparison is to the R108 genotype inoculated with the same rhizobial strain. ***P < 0.001.
(b–g) Photographs illustrating these infection phenotypes, both inoculated strains carrying a constitutive hemA‐lacZ reporter gene fusion (pXLGD4) for visualization of bacteria in blue. (b, c) R108/exoY; (d, e) R108/exoHKdel/exsH‐1345; (f, g) Mtlyk10/exoY; (h, i) Mtlyk10/exoHKdel/exsH‐1345. Scale bars = 100 µm.
