Figure 3.
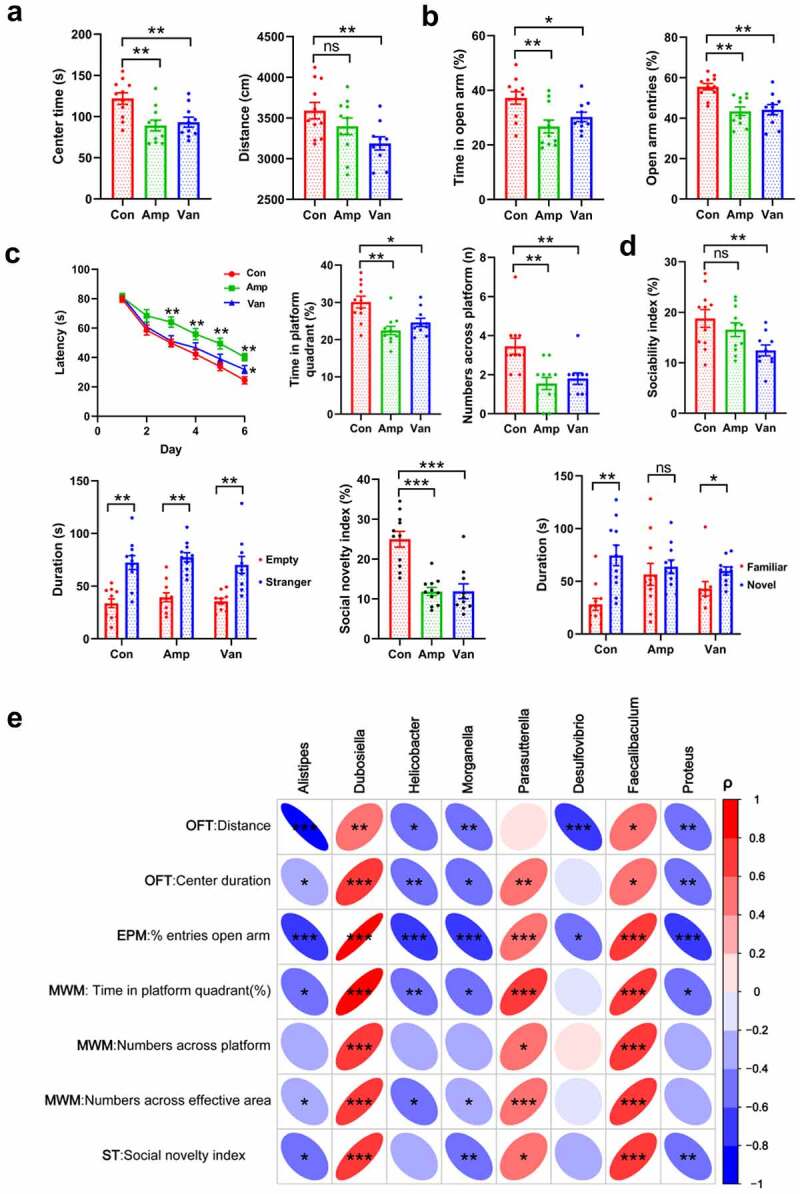
Gut dysbiosis increases the anxiety and impairs the spatial memory and social behavior(a, b) The locomotor and anxiety-like behavior in the OFT (A) and EPM test (B). N = 9–10/group. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, unpaired two-tailed t-test, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ns: no significance. (c) The spatial learning and memory ability were evaluated using the MWM test. N = 9–10/group. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, unpaired two-tailed t-test, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. (d) The figure shows the three-chambered social test, the sociability index and social novelty index were shown. N = 9–10/group. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, unpaired two-tailed t-test, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ns: no significance. (e) Spearman’s correlation analysis of the relationship between behavioral outcomes and the abundance of bacteria. Positive sloped elipses represents a positive correlation, negatively sloped ellipses indicates negative correlations. The color shows the strength of the spearman correlation coefficient ρ, ρ > 0.6 or ρ<-0.6, and P-value < 0.05 were considered as a significant correlation. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
