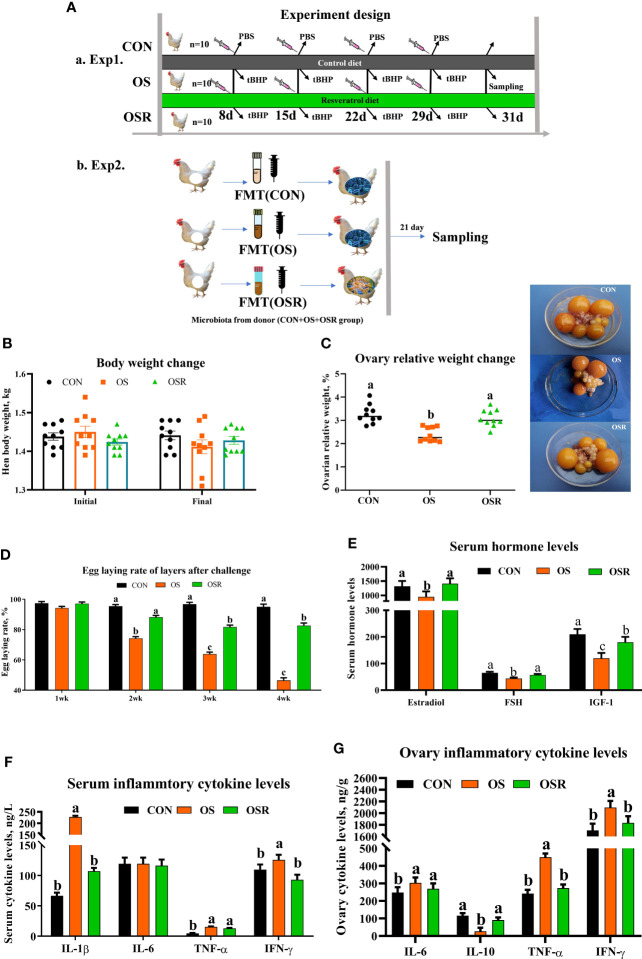
Figure 1.
Dietary resveratrol supplementation alleviated the oxidative stress (by tBHP) induced depression in egg-laying rates, reproductive hormones, and cytokine levels. Data are means ± SEM represented by vertical bars or plot individual values ± SEM. (A) Schematic illustration of the experimental design. a, in experiment 1, layers were fed the same basal diet for 24 days and with the tBHP (OS) or PBS (CON) injection at 9 AM on d 8, 15, and 21. The OSR group diet was supplemented with 600 mg/kg resveratrol added in CON treatment. b, in experiment 2, the microbiota-depleted layers were fed CON diet and received FMT from donor mice (n= 10/group) that were fed resveratrol. (B) Body weight change. (C) Ovary index. (D) Egg-laying rate after challenge. (F) Serum hormone levels. (G) Serum cytokine levels. (D) Ovary cytokine levels. CON, control; OS, oxidative stress (injection of 800 μmol/kg BW of tBHP); OSR, CON + 600 mg/kg resveratrol; FSH, follicle-stimulating hormone; IGF-1; insulin-like growth factor-1, IL-1β = interleukin-1 β; IL-6, interleukin-1, IL-10, interleukin-10; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha; IFN-γ, Interferon-γ. Statistical significance was evaluated by Tukey’s Test. p < 0.05.