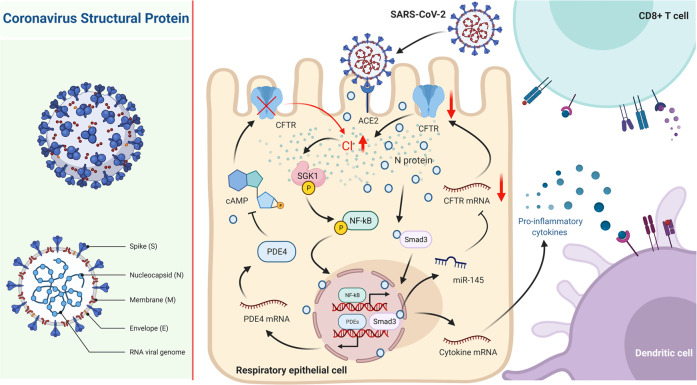
Fig. 8.
Schematic diagram depicting the role of intracellular Cl− accumulation in eliciting an ongoing inflammatory response after SARS-CoV-2 N protein stimulation in RECs. In RECs, the N protein interacted with Smad3, which triggered the downregulation of the CFTR via miR-145. Thereafter, the [Cl−]i was elevated and elicited inflammatory responses through activating the Cl−-sensing SGK1. Moreover, the expression of PDE4 was upregulated owing to the activation of NF-κB, which resulted in cAMP degradation and dysfunction of CFTR, contributing to the sustained high [Cl−]i and ongoing airway inflammation. [Created with BioRender.com (Canada)]