FIGURE 2.
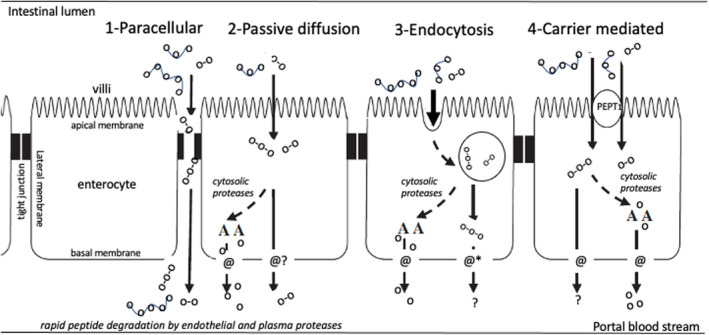
Potential pathways of amino acid and peptide absorption in the small intestine. (1) Paracellular through widened tight junctions, (2) passive diffusion through the enterocyte, (3) transcellular endocytosis, followed by carrier transport or suggested peptide cargo*‐permeability and (4) transcellular transport by carrier‐mediated passage (*It is unlikely that peptides will passively diffuse across the cell membrane, but altering their physical properties (such as conformational flexibility and polarity) has been proposed to improve their permeability, also referred to as peptide cargo (Yang & Hinner, 2015) figure modified from (Miner‐Williams et al., 2014))
