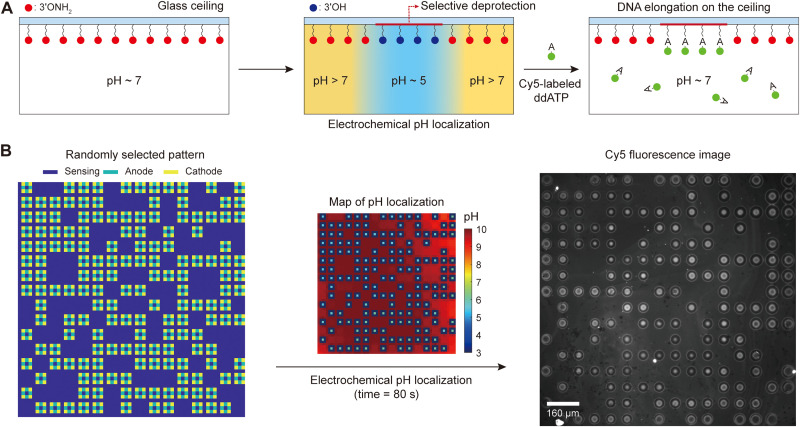
Fig. 5. Parallelizing pH-regulated enzymatic incorporation of nucleotides (ddATP) onto single-stranded DNA molecules.
(A) Schematic illustration of pH-regulated enzymatic incorporation of nucleotides to substrate DNA molecules on a glass ceiling with spatioselectivity. Localized pH control induces a spatioselective deprotection of DNA strands. These deprotected strands can then be enzymatically elongated with Cy5-labeled ddATP nucleotides in parallel. The ceiling height is about 14 μm. (B) After parallelized enzymatic incorporation of Cy5-labeled ddATP to spatioselectively deprotected sites, epifluorescence imaging shows that the Cy5 fluorescence pattern (right) matches the randomly selected current stimulation pattern (left) exactly, thus confirming the enzymatic incorporation of nucleotides at the spatioselectively deprotected sites. The pH map at the midpoint of the 80-s-long stimulation is shown in the middle.