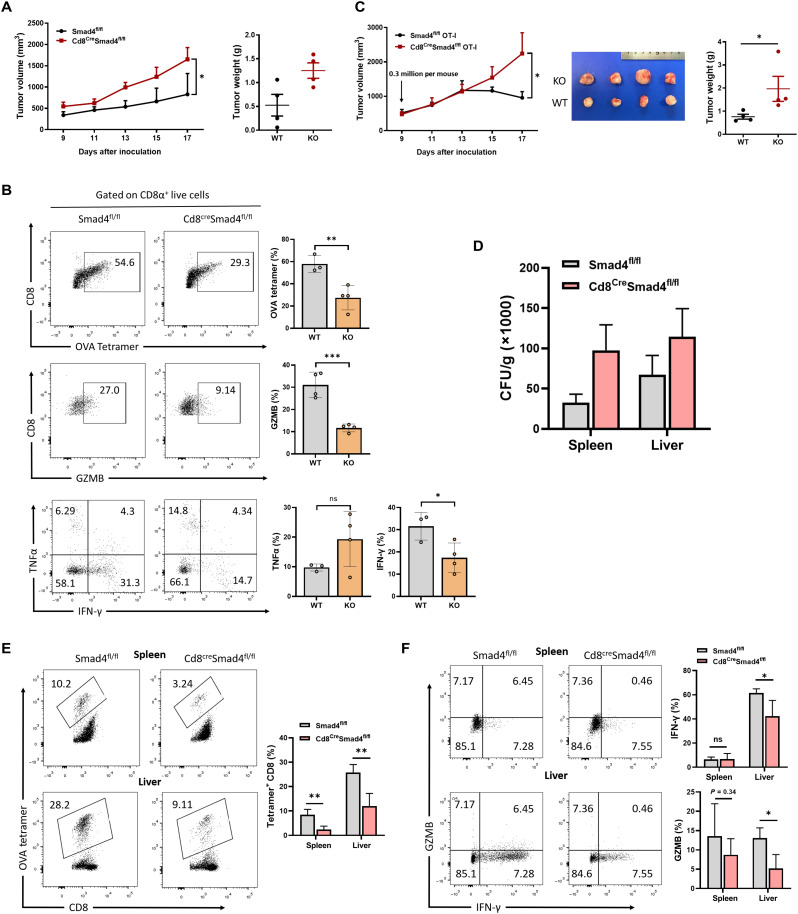
Fig. 1. SMAD4-deficient CD8+ T cells exhibit impaired cytotoxic function.
(A) E.G7 cells (1 × 106 cells per mouse) were inoculated subcutaneously into WT (n = 5) and Cd8CreSmad4fl/fl mice (n = 5). Tumor growth was monitored from day 9 after inoculation. (B) TILs were isolated at day 17 from E.G7-bearing mice. OVA-specific CD8+ T cell percentages and GZMB, TNFα, and IFN-γ expression in CD8+ TILs were analyzed by flow cytometry. (C) Left: Growth of E.G7 tumor in mice receiving WT or Smad4-deficient OT-I cells (3 × 105 cells per mouse). Right: Representative images of tumors, 17 days after transplant. KO, knockout. (D) OVA-modified L. monocytogenes (LM-OVA) colony-forming units (CFUs) from spleens and livers were calculated at day 8 after infection. (E) The percentages of OVA-specific CD8+ T cells in spleens and livers from LM-OVA–infected WT (n = 5) or Cd8CreSmad4fl/fl mice (n = 5). Measured by flow cytometry. (F) Expression levels of GZMB and IFN-γ in CD8+ T cells from LM-OVA–infected WT or Cd8CreSmad4fl/fl mice. These experiments were repeated three times. Data are represented as means ± SEM. ns, not significant. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.