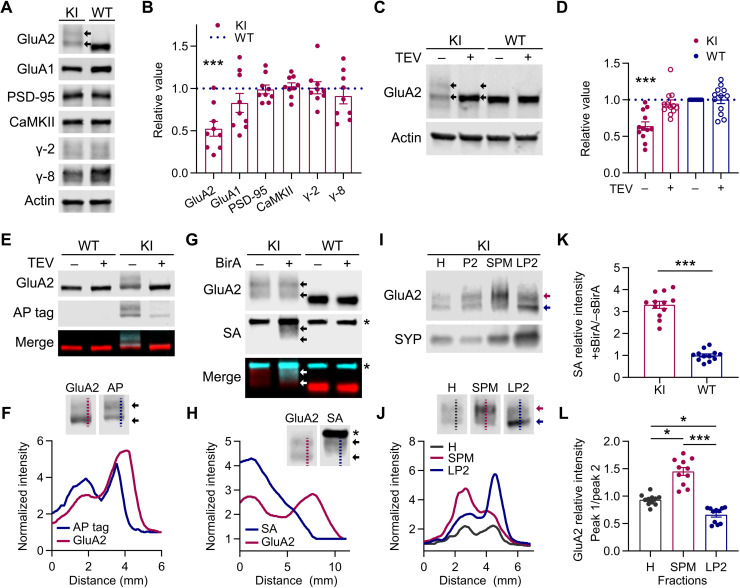
Fig. 5. Biochemical characterization of AP-GluA2 expression and localization.
(A) Representative Western blots of AP-GluA2 KI or WT protein samples (whole brain or hippocampal lysate). Double banding is observed for AP-GluA2 KI (arrows). (B) Quantification of KI protein expression relative to WT and normalized to β-actin loading control. N = 9. ***P = 0.0006 (one-sample t tests). (C) In vitro incubation of KI or WT protein samples with TEV protease cleaves the AP tag and resolves GluA2 to a single band (arrows) with the same relative expression as WT. (D) Quantification of GluA2 expression relative to WT (−TEV) and normalized to β-actin loading control. N = 12. ***P = 0.0005 (Wilcoxon signed-rank test). (E) Dual labeling of AP tag and GluA2 in WT or KI protein samples with or without TEV protease. (F) Line scans (dashed lines in insets) reveal partial colocalization of AP tag and lower GluA2 band (arrows). (G) In vitro incubation of KI or WT protein samples with sBirA + biotin-AMP; SA binds bAP-GluA2 in the upper GluA2 band (arrows). Asterisks denote SA binding to endogenous biotin binding proteins. (H) Line scans reveal colocalization of SA with the upper but not lower GluA2 band. (I) Subcellular fractionation of hippocampal lysate (H, homogenate; P2, crude membranes) shows enrichment of the upper AP-GluA2 band in the synaptic plasma membrane fraction (SPM) and the lower band in the vesicular fraction (LP2). (J) Line scans show differential sorting of AP-GluA2 populations to the membrane (SPM, red line and arrow) and intracellular vesicles (LP2, blue line and arrow). (K) Quantification of SA binding (+sBirA relative to −sBirA). N = 12. ***P < 0.0001 (unpaired t test). (L) Quantification of relative AP-GluA2 distribution (upper, peak 1; lower, peak 2) in line scans from blots of hippocampal lysate (H), membrane (SPM), and vesicular (LP2) fractions. N = 11. *P ≤ 0.0337, and ***P ≤ 0.0001 (Kruskal-Wallis test; F = 27.08, P < 0.0001; Dunn’s post hoc test). See also figs. S14 to S17.