FIGURE 2. A Proposed Treatment Approach for Advanced-Stage FL.
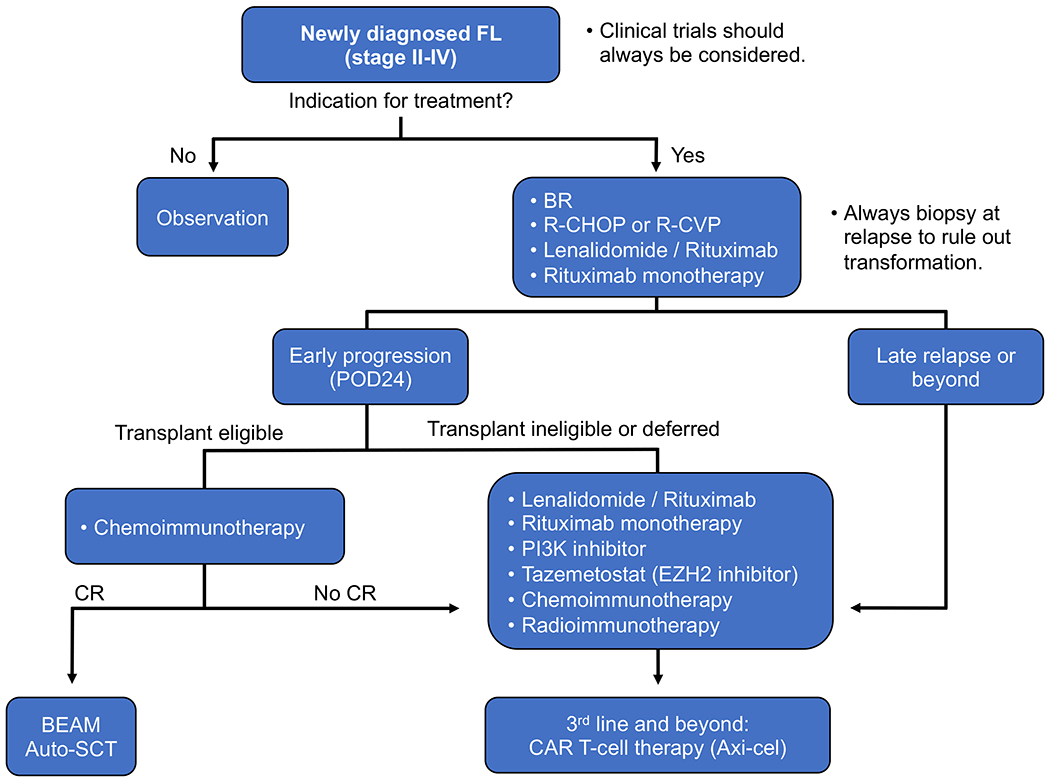
Unless there is an indication for treatment based on GELF or NCCN criteria, patients may be observed. When treatment is indicated, clinical trials should always be considered. Standard therapy includes chemoimmunotherapy with BR, which is the most common, and has improved PFS with less toxicity compared to R-CHOP. Lenalidomide with rituximab is an excellent first-line or second-line option, but this combination requires longer treatment duration than R-CHOP or BR. Rituximab monotherapy is also effective in the frontline and relapsed/refractory setting, especially with low disease burden. Patients with early relapse within 24 months (POD24) are a high-risk subset. Salvage chemoimmunotherapy includes bendamustine or CHOP with an anti-CD20 agent, followed by auto-SCT. Targeted agents such as PI3K inhibitors and tazemetostat may also be used. The optimal sequence of subsequent-line agents is unknown, and there are multiple options that can be used prior to CAR T-cell therapy, which is approved after 2 or more lines of therapy.
auto-SCT, autologous stem cell transplant; BEAM, BCNU (carmustine), etoposide, cytarabine, and melphalan; BR, bendamustine and rituximab; CHOP, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone; CR, complete remission; FL, follicular lymphoma; R-CHOP, rituximab with CHOP.
