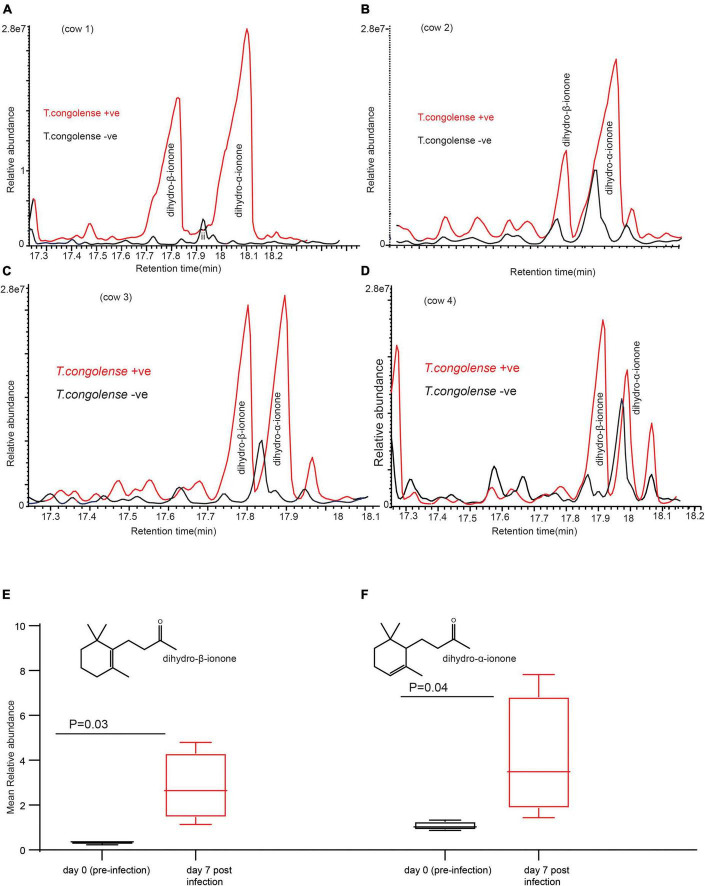
FIGURE 3.
Trypanosoma congolense infection induced dihydro-β-ionone in urine metabolites. (A–D) GC-MS profiles showing dihydro-β-ionone and dihydro-α-ionone levels in T. congolense-uninfected and infected cows, and (E) graph showing the significant change in abundance of dihydro-β-ionone due to T. congolense infection (F). Graph showing the significant change in a relative abundance of dihydro-α-ionone due to T. congolense infection. Y-axis in (A–D) is the area of the peak, which reflects the amount of a given compound. The size and area of the component peak are proportional to the amount of the component reaching the detector. X-axis in (A–D) is retention time in minute, which is a measure of the time taken for a compound to pass through a chromatography column. It is calculated as the time from injection to detection.