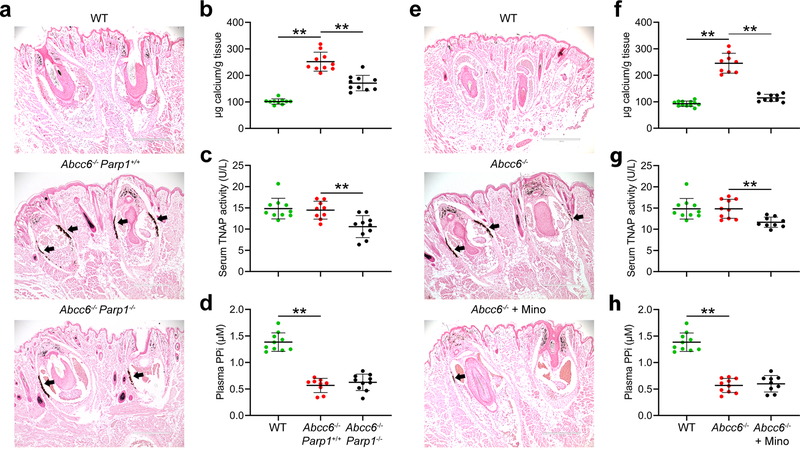
Figure 2. Genetic and pharmacologic studies show that abolished PARP1 activity in the Parp1−/− mice inhibits ectopic connective tissue calcification in the Abcc6−/− mice. All mice were analyzed at 12 weeks of age. (a-d), genetic proof-of-concept study. (e-h), minocycline treatment study.
(a) Muzzle skin biopsy samples were collected and processed for histopathology, followed by von Kossa stains. The WT mice were negative for ectopic calcification (top panel). The Abcc6−/−Parp1−/− mice (bottom panel) developed less ectopic calcification of the dermal connective tissue sheath of vibrissae in the muzzle skin compared with Abcc6−/−Parp1+/+ mice (middle panel). (b) The calcium content in the muzzle skin of Abcc6−/−Parp1−/− mice was significantly decreased compared with Abcc6−/−Parp1+/+ mice. (c) Serum TNAP activity was significantly reduced in Abcc6−/−Parp1−/− mice. (d) Plasma PPi levels in the Abcc6−/−Parp1+/+ mice were 43% of those in wild-type mice; however, plasma PPi levels in the Abcc6−/−Parp1−/− mice were not statistically different from those in Abcc6−/−Parp1+/+ mice. (e) The Abcc6−/− mice treated with 100 mg/kg/day minocycline had marked decrease of calcification (bottom panel), as compared to untreated Abcc6−/−mice (middle panel). (f) The chemical assay of calcium showed significant reduction in the amount of calcium in the muzzle skin in the Abcc6−/− mice treated with 100 mg/kg/day minocycline. (g) Serum TNAP activity was significantly decreased in Abcc6−/− mice as a result of minocycline treatment. (h) Plasma PPi levels in the Abcc6−/− mice treated with minocycline were not statistically different from those in Abcc6−/− control mice. n = 9–12 mice per group. Bar = 400 μm. Mino, minocycline; PPi, inorganic pyrophosphate; TNAP, tissue non-specific alkaline phosphatase; WT, wild-type. **P < 0.01.