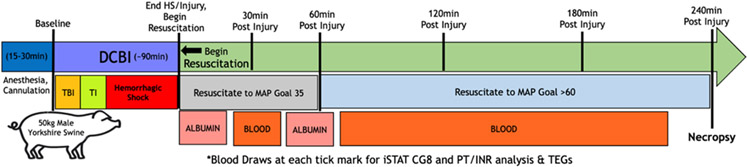
Figure 1. Graphical representation of experiment.
Following anesthesia and initial vascular and intracranial access, swine were either subjected a SHAM model (consisting of surgical access and instrumentation only) or to the dismounted complex blast injury (DCBI: consisting of blast TBI, tissue injury caused by bilateral femur fractures, and then a pressure targeted hemorrhagic shock phase). The SHAM group remained under anesthesia and monitored during the time it takes to complete the entire DCBI series. At the end of the hemorrhagic shock phase, DCBI swine are monitored for 240min during which resuscitation occurs. SHAM swine complete 240min of observation with normal saline for fluid replacement for insensible losses.