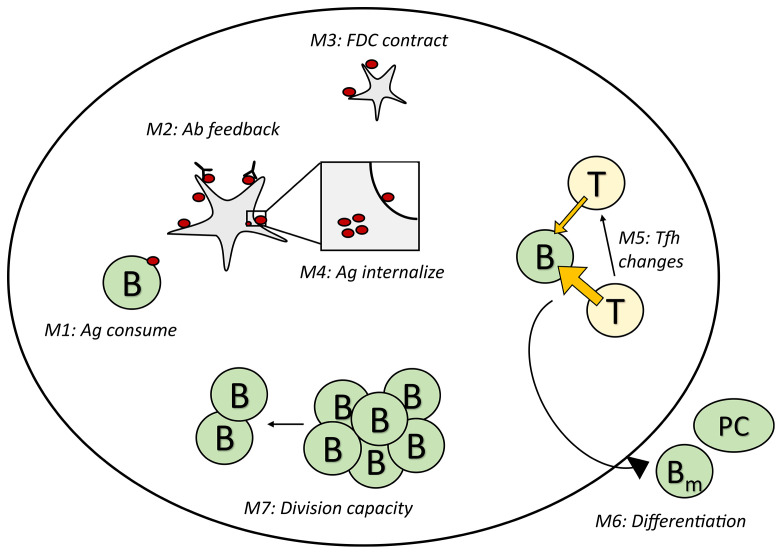
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the GC shutdown mechanisms. In mechanisms M1-M4, antigen limitation arises due to the consumption of antigen by B cells, masking of antigen by soluble antibodies (antibody feedback), contraction of FDC network and changes in antigen cycling rate constants leading to increased internalization of antigen, respectively. In M5, Tfh signaling intensity decreases leading to limiting T cell help. In M6, increased terminal differentiation of GC B cells into memory/plasma cells leads to increased exit from GCs. In M7, B cells have limited capacity to divide leading to decreased proliferation over time. GC, Germinal center; FDC, Follicular Dendritic Cell; T/Tfh, T follicular helper cell; Ab, Antibody; Ag, Antigen; PC, Plasma cell; Bm, Memory B cell; B, Germinal center B cell.