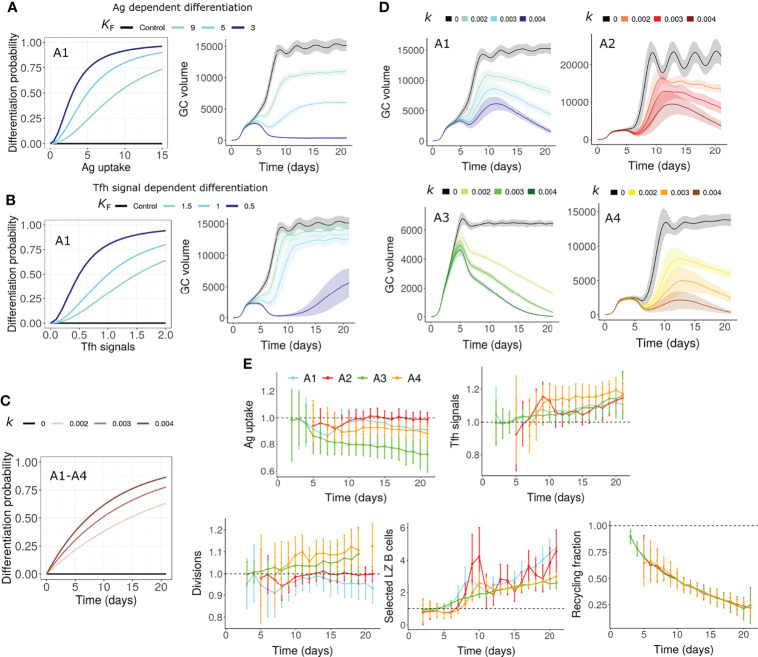
Figure 4.
GC shutdown due to terminal differentiation of B cells (Mechanism 6). (A, B) Differentiation probability in antigen dependent (A) and Tfh signal dependent (B) terminal differentiation and corresponding GC volume dynamics. Colors represent different values of K F in Equation 9. K F is the amount of Ag captured (in antigen dependent terminal differentiation) or Tfh signals received (in Tfh signal dependent terminal differentiation) for half-maximal differentiation probability (see Methods). Assumption A1 was considered in these simulations. (C, D) Terminal differentiation probability vs time according to Equation 10 in assumptions A1-A4 for time dependent terminal differentiation (C). Colors represent different values of k and corresponding GC dynamics (D). Black curves represent control simulations. Different colors represent value of k in Equation 10 and are shown in labels above (C, D) Value of k controls the increase in differentiation probability. Solid lines and shaded regions in panels A, B and D represent mean and standard deviation of 50 simulations, respectively. (E) Average antigen uptake per B cell, Tfh signals acquired per B cell, average number of divisions per recycling GC B cell and fraction of Tfh selected LZ B cells for time dependent terminal differentiation (k = 0.003). Readouts were normalized with that of the control simulation. Colors represent the assumptions A1-A4. Error bars represent standard deviation of 50 simulations. GC, Germinal center; Tfh, T follicular helper cell; Ag, Antigen; LZ, Light Zone.