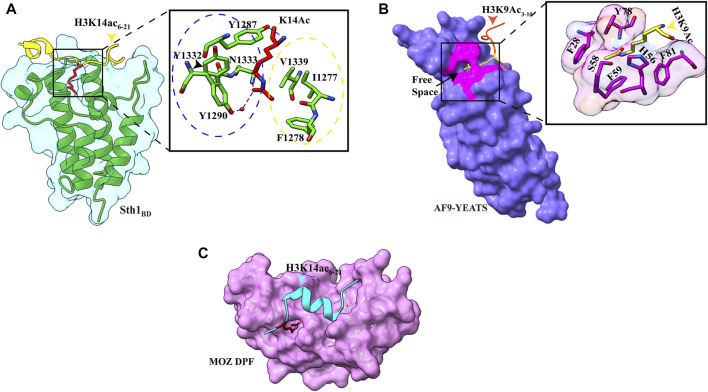
FIGURE 2.
Readout of acetyllysine by different readers. (A) Left: overall structure of Sth1BD (green ribbons) with H3K14ac6–21 (yellow color, K14 shown as red sticks). Right: close-up view of H3K14ac-binding sites of Sth1. H3K14Ac is shown in red color, and Sth1BD residues are shown in green color. Residues in the blue circle interact with the aliphatic side chain of K14, while residues in the yellow circle interact with the methyl group of acetyl mark. Hydrogen bonds are shown as blue dashed line (PDB ID: 6KMJ). (B) Left: overall structure of the AF9 YEATS domain (purple color) with H3K9Ac3–10 (orange–red color, K9 shown in yellow color). K9ac (yellow color) can be seen inserted into the narrow end-open pocket. Right: close-up view of interacting residues of H3K9Ac (yellow color) and AF9 residues (pink color). A serine (S58)-lined aromatic cage (F28, H56, F59, Y78, and F81) is formed in which the acetylated lysine snugly fits (PDB ID: 4TMP). (C). Overall structure of H3K14Ac3–15 (stick model in cyan color) with MOZDPF (pink surface). K14ac (red color) can be seen inserted in the “dead end” pocket of MOZ protein (PDB ID: 4LLB).