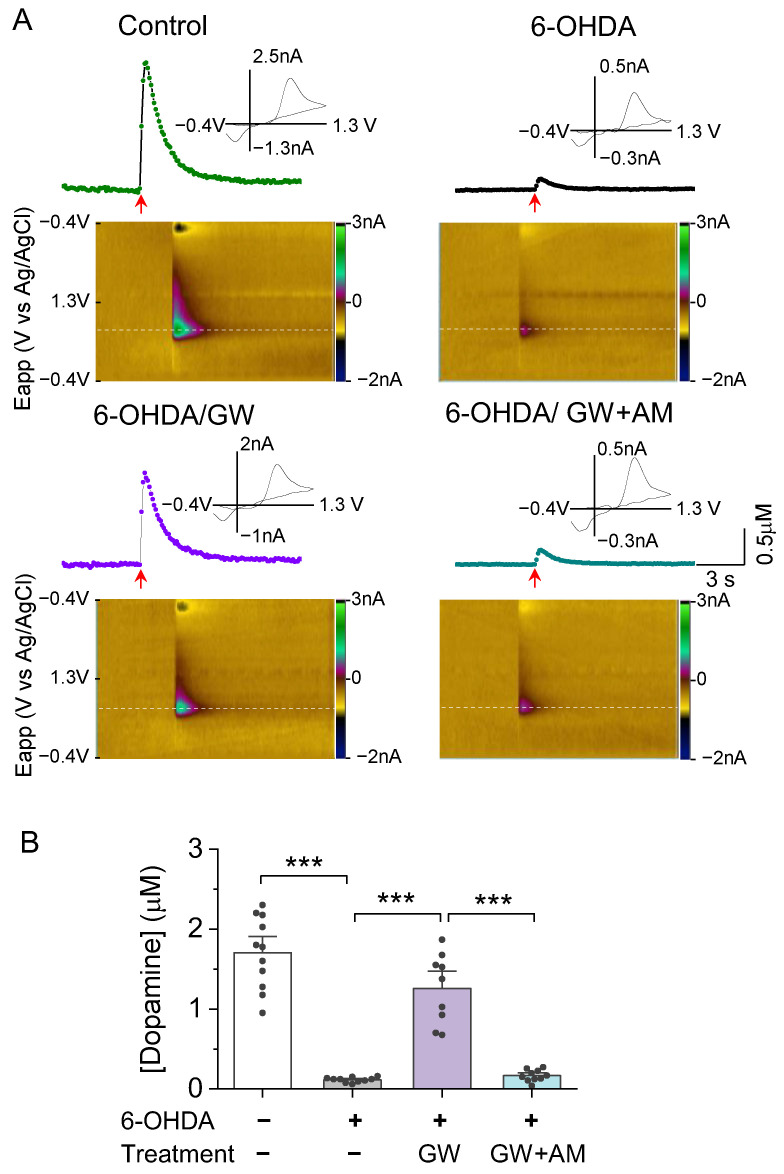
Figure 3.
GW protected against 6OHDAinduced loss of evoked dopamine release in the NAc in vitro. (A) Concentration trace (top) and color plot (bottom) for dopamine release triggered by electrical stimulation of the NAc shell in slices from mice in the control and treatment groups. (B) Summarized data indicate that there was a significant decrease in evoked dopamine release in the 6-OHDA group relative to the control (*** p < 0.001; n = 10–11 slices from 3–4 mice). Chronic treatment with GW reduced 6-OHDA-induced loss of evoked dopamine release (*** p < 0.001; n = 9–10 slices from 3–3 mice), which was blocked by AM (*** p < 0.001; n = 9–10 slices from 3–3 mice).