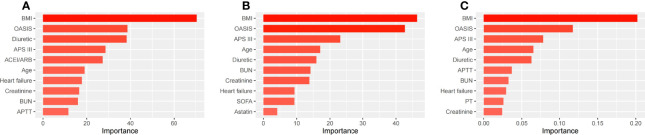
Figure 5.
The top ten important factors of SA-AKI for men in the decision tree model (A), random forest model (B) and extreme gradient boosting model (C). Models were adjusted for all variables, including age, BMI, ethnicity, admission type, hypertension, coronary atherosclerosis, heart failure, diabetes mellitus, COPD, cerebral infarction, chronic liver disease, chronic kidney disease, tumor, APS III, OASIS, SOFA, heart rate, MAP, RR, temperature, SpO2, WBC, hemoglobin, platelet, PH, bicarbonate, BUN, creatinine, potassium, sodium, chloride, glucose, PT, APTT, lactate, vasopressor use, mechanical ventilation use, diuretic, aminoglycoside, statin, ACEI/ARBs. ACEI/ARBs, Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors/angiotensin receptor blockers; AKI, Acute kidney injury; APS III, Acute Physiology Score III; APTT, Activated partial thromboplastin time; BMI, Body mass index; BUN, Blood urea nitrogen; COPD, Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; OASIS, Oxford Acute Severity of Illness Score; PT, Prothrombin time; SA-AKI, Sepsis associated acute kidney injury; SOFA, Sequential Organ Failure Assessment; RR, Respiratory rate; WBC, White blood cell.