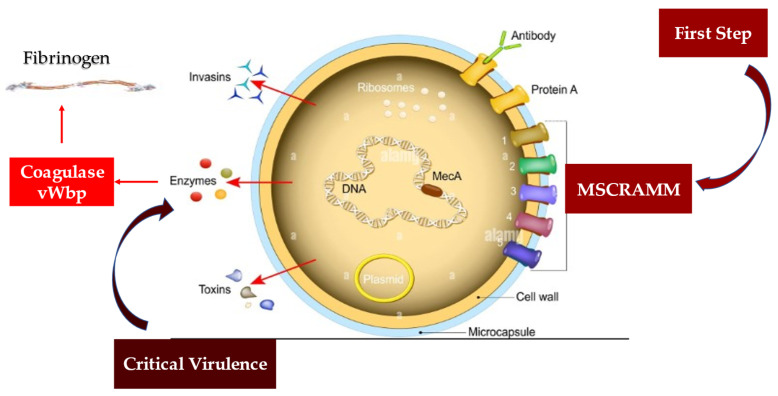
Figure 6.
Depiction of virulent factors of S. aureus. MSCRAMMs have a substantial key role in driving the initiation of endovascular, bone and joint, and prosthetic device infections. These structures can bind to molecules such as collagen (mostly via Cna), fibronectin (via FnbAB), and fibrinogen (with ClfAB and Fib), and thus evade the immune system. The development of infection is induced by Coa and von Willebrand factor-binding protein that led to critical virulence. Coa binds preferentially to soluble fibrinogen, while vWbp does not disclose any preference between the two forms of fibrinogen. Abbreviations: Clf, cell-bound clumping factor; Coa, coagulase; Fnb, fibronectin binding protein; MSCRAMM, microbial surface components recognizing adhesive matrix molecules; vWbp, von Willebrand factor-binding protein.