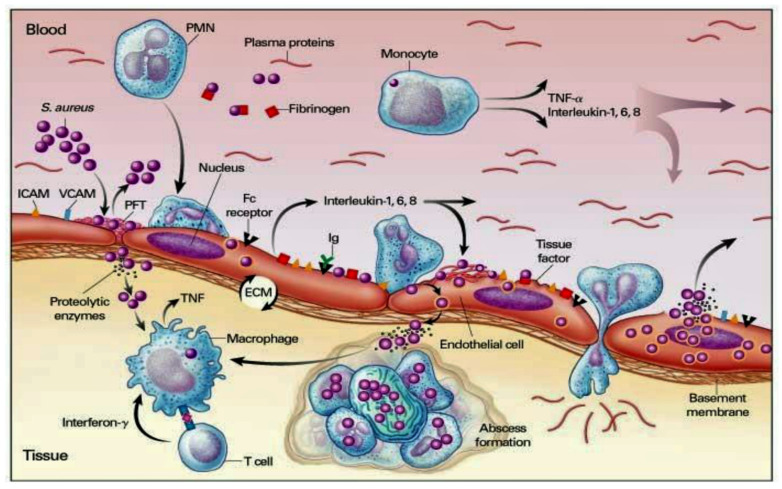
Figure 7.
Bacterial adhesion induces the pathophysiological process of infective endocarditis. The first step led to inflammatory response with the involvement of inflammatory cells (PMN, monocyte, and macrophage). The inflammation is mediated by the production of cytokines (TNF, α, Il 1,6 and 8), integrins, tissue factor, and adhesion molecules (ICAM, VCAM), which in turn attract monocytes and platelets with associated production of fibronectin, due to the effect induced by chemokines. S. Aureus releases Cytoxins that trigger the immunity response both innate and mediate (T-cell and B-cell). Abbreviations: ICAM, Inter Cellular Adhesion Molecule; S. Aureus, Staphylococcus aureus; IL; interleukine; PMN, polymorphonuclear; TNF, tumor necrosis factor; VCAM, vascular cell adhesion molecule.