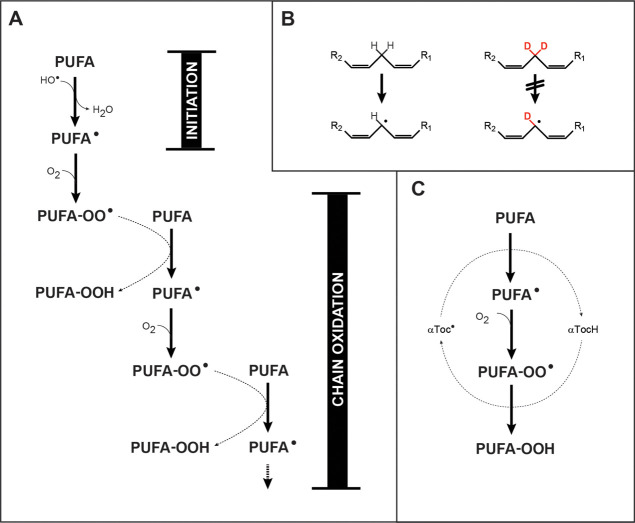
Figure 1.
Chemical mechanisms. (A) PUFA peroxidation may be initiated by •OH radicals, and propagated indefinitely by a chain reaction in the presence of oxygen. The chain reaction is linear, that is, non-branching, so that oxidative damage does not necessarily accelerate with time, except insofar as additional chain reactions are initiated. It should be noted that PUFA-OOH species are unstable and may undergo spontaneous internal rearrangements and cleavages, as well as oxidations and reductions. (B) Bis-allylic PUFA hydrogens are readily abstracted by •OH radicals to yield a carbon-centered free radical; this process is markedly inhibited by deuterium substitution. (C) Under some conditions, a bis-allylic hydrogen may be abstracted by an α-tocopheryl radical, with regeneration of α-tocopherol in the course of peroxide formation.