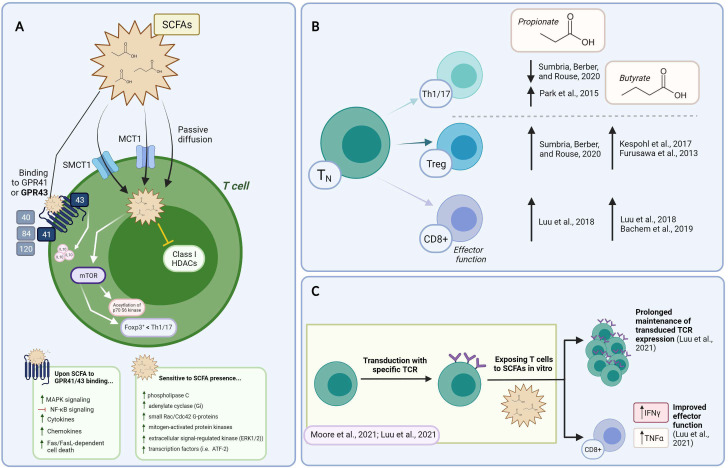
Figure 2.
Constructing the mechanism of action and the impact of SCFAs on T cell functions in vitro. (A) Summary of SCFAs mechanism of action in T cells. The ability of SCFA to freely diffuse across the plasma membrane, be transported or bind to GPCR is shown. Their reported mechanism of action mediated by intracellular signaling events and HDAC is also depicted. (B) Supplementing T cell cultures with SCFAs impacts on Th1/17, Treg, and CD8+ T cell functional phenotypes (described within the text). Supporting references are indicated. (C) Exploiting SCFA over the course of TCR/CAR-T manufacturing. Data supports the ability of SCFAs to prolong transgene expression and increase effector functions. CAR, chimeric antigen receptor; HADS, histone deacetylase; SCFAs, short-chain fatty acids;