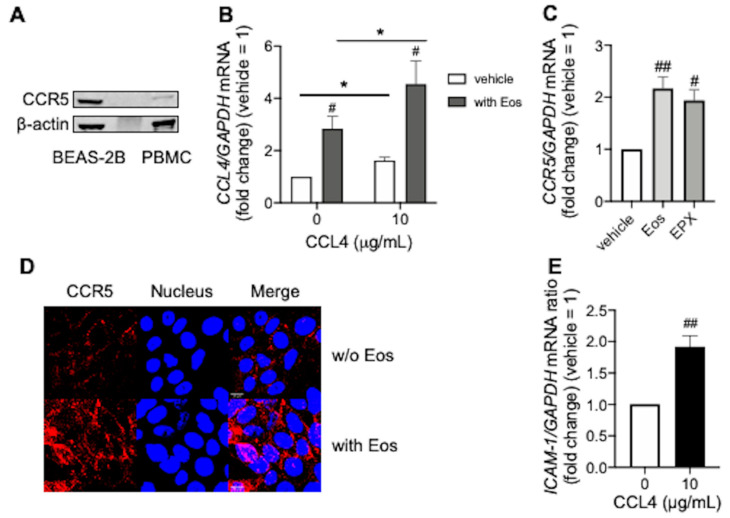
Figure 3.
Autocrine effects of CCL4 during eosinophilic inflammation. (A) CCR5 expression in BEAS-2B cells. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were used as a positive control. Experiments were repeated at least three times with different cell preparations. (B) CCL4 mRNA levels in BEAS-2B cells co-incubated overnight with CCL4 and/or purified peripheral blood eosinophils. (C) CCR5 mRNA levels in BEAS-2B cells co-incubated overnight with purified peripheral blood eosinophils, or EPX (10 µg/mL) for 48 h. (D) CCR5 expression in BEAS-2B cells co-incubated overnight with purified peripheral blood eosinophils. CCR5 (red) and the nucleus (blue) are shown in upper (without eosinophils) and in lower (with eosinophils) panels, respectively. Images were obtained using a FV3000 confocal microscope (400× objective). Scale bars in the bottom-left corner of Merge indicate 10 μm. Results were representative of at least three experiments. Values in (B,C,E) represent the mean ± standard error of the mean from four experiments; # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01 (vs. vehicle in each group), * p < 0.05 (as shown between the two groups).