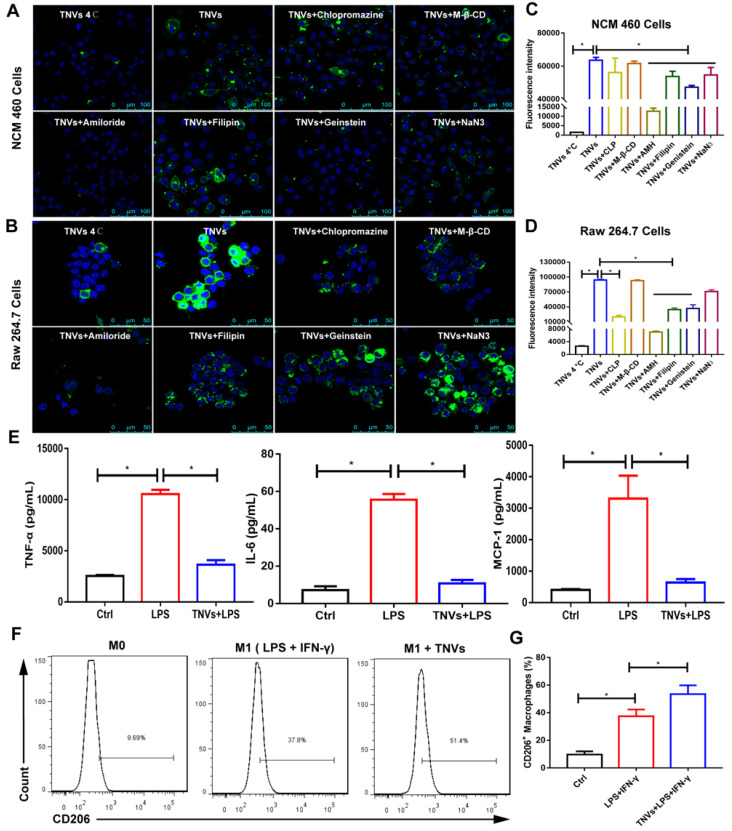
Figure 3.
In vitro cell internalization mechanisms, anti-inflammatory properties and the effect on the macrophage polarization of TNVs. A-B. Representative fluorescence images of cellular uptake of DiO-labeled TNVs in NCM 460 cells and Raw 264.7 macrophages after co-incubation for 6 h and additional different inhibitors treatment 1 h. C-D. Fluorescence intensity of cellular uptake of DiO-labeled TNVs in NCM 460 cells and Raw 264.7 macrophages determined using flow cytometry. E. In vitro anti-inflammatory activities of TNVs on Raw 264.7 macrophages. The concentrations of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, and MCP-1) were quantified using ELISA assay. F-G. Flowcytometry analysis of CD206 expression in Raw 264.7 macrophages. Data are shown as mean ± SD, n = 3. Significance as *P < 0.05.