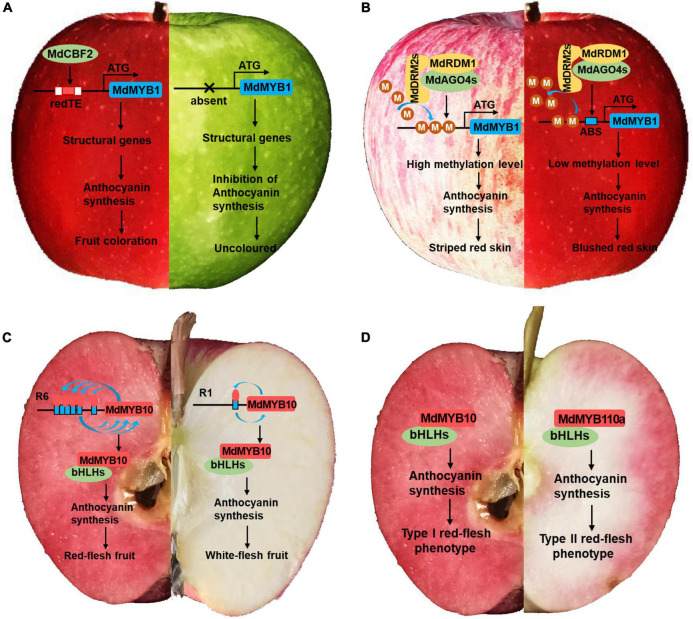
FIGURE 2.
Red pigmentation of apple fruit skin and flesh. (A) A gypsy-like long terminal repeat retrotransposon (designated redTE) was inserted 3297 bp upstream of MdMYB1, thereby activating the expression of MdMYB1 and controlling the redness of the fruit skin. (B) MdAGO4s, MdDRM2s, and MdRDM1 interact with each other and form an effector complex. MdAGO4s recruit MdDRM2s, which catalyze CHH methylation of the MdMYB1 promoter. MdMYB1 then regulates anthocyanin accumulation to determine the coloration. M, a -CH3 (methyl); ABS, AGO4 binding sequence. (C) Model showing autoregulation of the R6 and R1 promoters by MdMYB10. The MdMYB10 promoter in red-fleshed apple contains six 23 bp repeating microsatellite sequences (R6), which confer MdMYB10 with self-activation. The MdMYB10 promoter in white-fleshed apple contains only one 23 bp repeating microsatellite sequence. (D) MdMYB10 and its homolog MdMYB110a are involved in the red pigmentation of type I and type II red-fleshed apples, respectively.