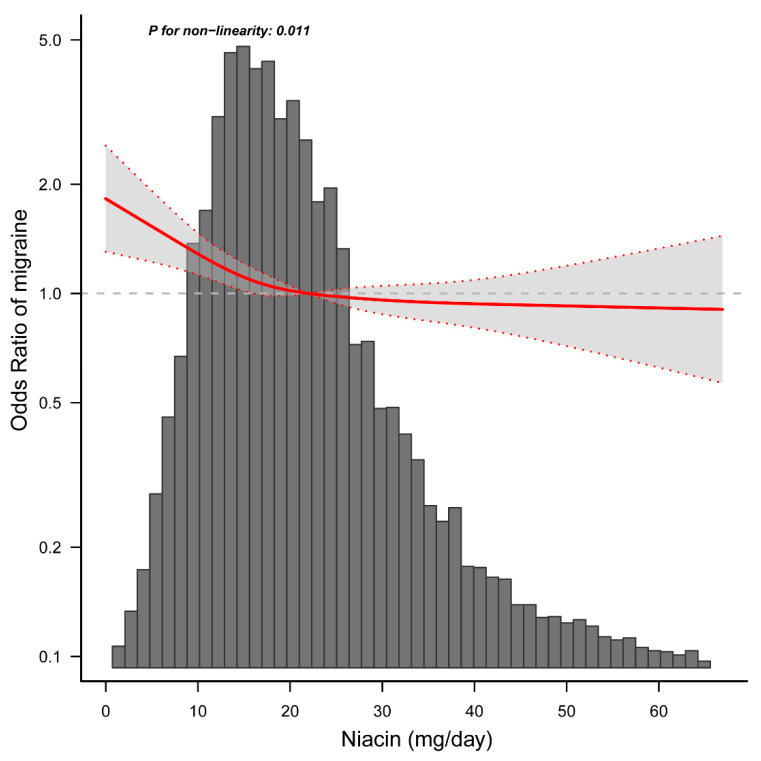
Figure 2.
Association between dietary niacin intake and migraine odds ratio. Solid and dashed lines represent the predicted value and 95% confidence intervals. They were adjusted for age, sex, marital status, race/ethnicity, education level, family income, smoking status, physical activity, hypertension, diabetes, stroke, coronary heart disease, body mass index, energy consumption, protein consumption, carbohydrate consumption, fat consumption, dietary supplements taken, and C-reactive protein. Only 99% of the data is shown.