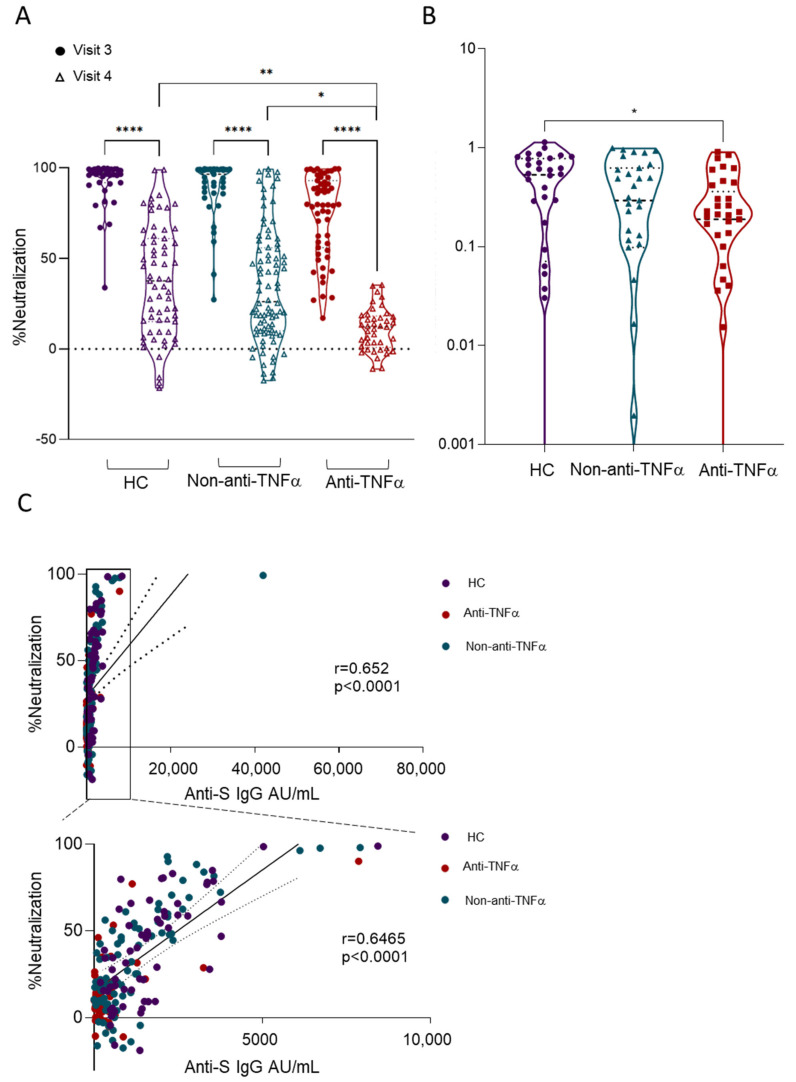
Figure 3.
Patients with IBD treated with anti-TNFα had significantly reduced levels of anti-SARS-CoV-2-neutralizing activity 6 months after two BNT162b2 vaccine doses. (A) Sera, diluted to a final concentration of 1:200 from healthy controls (HCs, shown in purple), patients with IBD receiving non-anti-TNFα treatment (non-anti-TNFα, shown in blue) and patients with IBD receiving anti-TNFα treatment (anti-TNFα, shown in red) were incubated with VSV-spike pseudo-particles (VSV∆GGFPS∆19) for 1 h in 37 °C, prior to infecting ACE2 expressing HEK293 cells for 24 h. The number of GFP-positive cells was normalized and converted to a neutralization percentage in each sample, compared to the average of control samples. Visit 3 (filled circles), visit 4 (open triangles)—after two vaccine doses, 1 and 6 months, respectively. (B) Ratio between visit 4 and visit 3 anti-SARS-CoV-neutralizing activity. Statistical analysis was carried out using independent sample Kruskal–Wallis test. *—p < 0.05, **—p< 0.01, ****—p < 0.0001. Black solid line denotes median, black dashed line denotes IQR 25-75. (C) Correlations between anti-S level and neutralizing activity. Abbreviations: VSV—vesicular stomatitis virus; ACE2—angiotensin-converting enzyme-2; RBD—receptor-binding domain; HEK—human embryonic kidney.