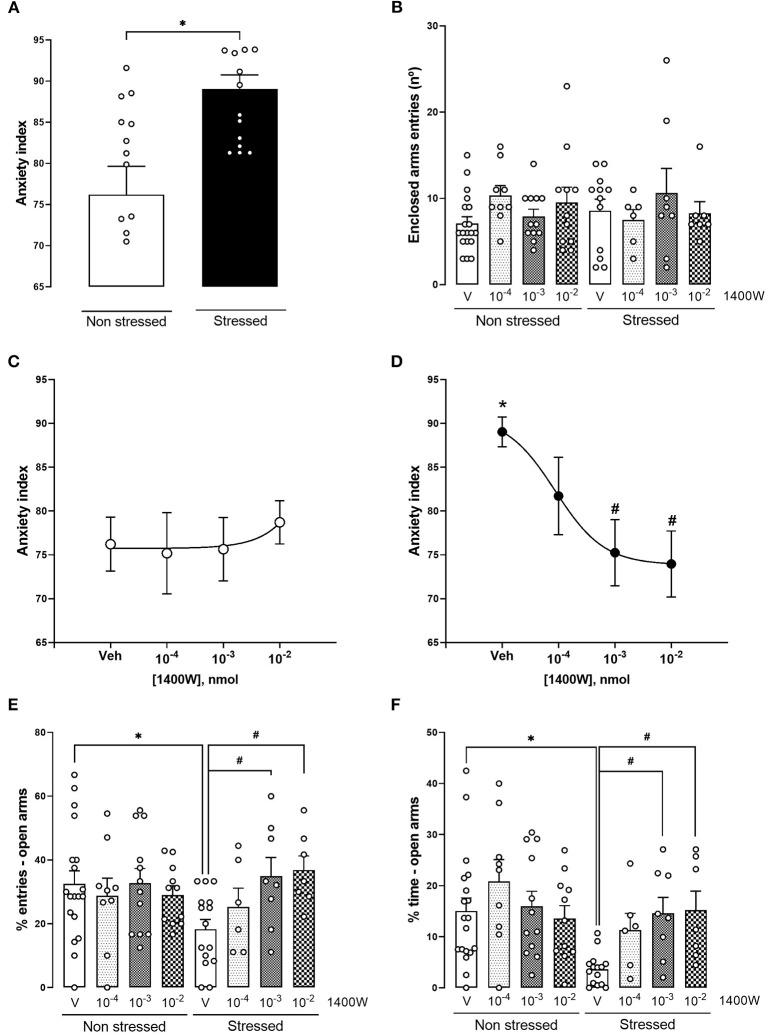
Figure 3.
iNOS inhibition reversed the anxiety behavior induced by acute restraint stress (RS) 24 h later in the elevated plus-maze (A). 1400 W microinjections did not affect naïve animals' behavior (C). 1400 W microinjections, at the doses of 10−3 and 10−2 nmol in stressed animals, prevented the anxiogenic-like behavior represented by a decrease in the anxiety index (D) and increase in the percentage of entries (E) and time (F) in the open arms of the maze. Also, stress and the treatments did not alter the number of entries in the closed arms (B). Each point/bar represents the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). *Indicates p <0.05 compared to the naïve vehicle group and #Indicates p < 0.5 compared to the stressed vehicle group (one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Tukey's post hoc test). n = 19, 9, 12, and 11 for naïve animals treated with vehicle, 1400 W 10−4, 1400 W 10−3, and 1400 W 10−2, respectively, and 15, 6, 8, and 7 for stressed animals treated with vehicle, 1400 W 10−4, 1400 W 10−3, and 1400 W 10−2, respectively.