Table 1.
Sleep stages and their electroencephalographic features.
| Category | Stages | EEG | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep | Stage 1 (N1) |
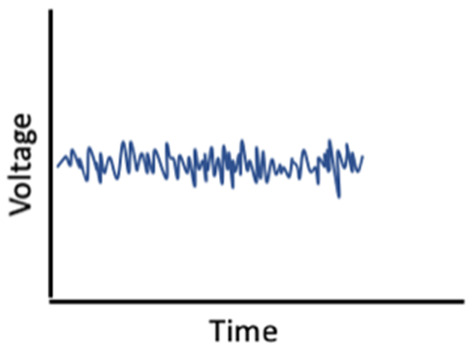
|
Lightest sleep stage, a transition between wake and sleep Easy to rouse a sleeper in N1 Wave Type: Alpha (8–12 Hz) Theta (47#x02013;7 Hz) |
| Stage 2 (N2) |
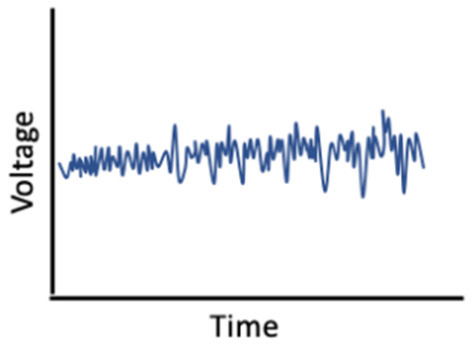
|
Heart rate and body temperature drop Features sleep spindles and K-complexes (see below) Harder to rouse than in N1 Wave type: Theta (4–7 Hz) Spindles (117#x02013;15 Hz); K-Complexes (12–15 Hz) | |
| Stage 3 (N3) |
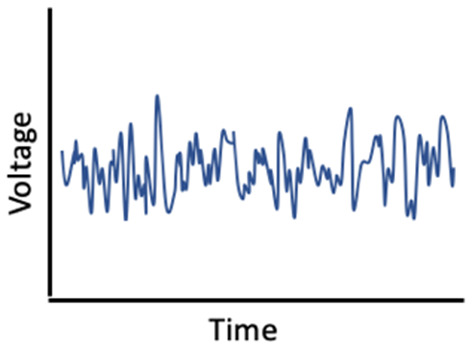
|
Also known as slow-wave sleep (SWS) Deepest sleep stage, hardest to rouse sleepers in N3 Wave type: Delta (0.5–2 Hz) Theta (4–7 Hz) Amplitude: >75μV | |
| Rapid eye movement (REM) sleep | REM |
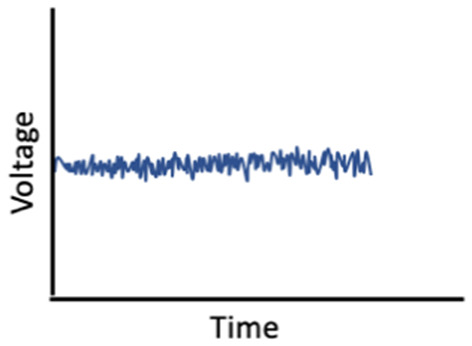
|
Rapid eye movement Most muscles paralyzed More desynchronized neuronal activity Wave type: Theta (4–7 Hz) Beta (15–35 Hz) |
| Sleep electroencephalogram (EEG) features | Sleep spindles |
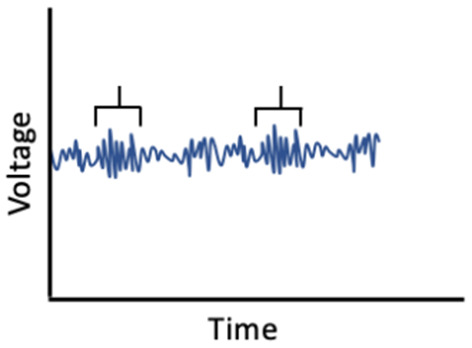
|
Brief spurts of synchronized brain activity in thalamocortical circuits Observed during N2 sleep Frequency: (11–15 Hz) |
| K complexes |
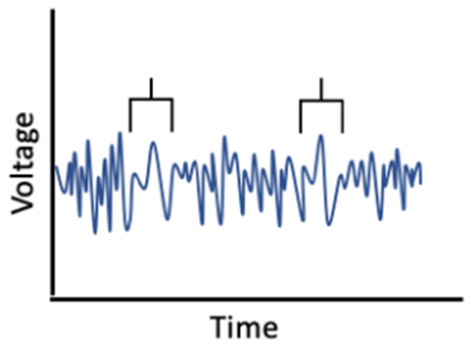
|
Waveforms primarily observed in the cortex during N2 sleep Frequency: (12–15 Hz) | |
| Slow oscillations |
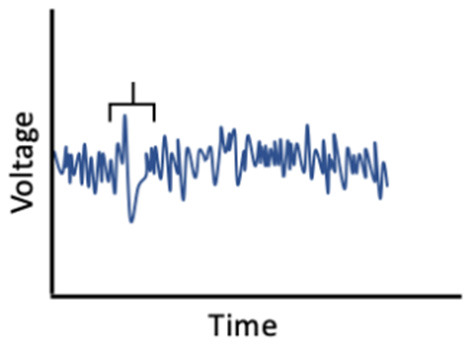
|
Reflect alternations between hyperpolarization (cortical neurons inactive) and depolarization (cortical neurons highly active) Observed during N3 sleep Frequency: (0.5–1 Hz) |
