Figure 5.
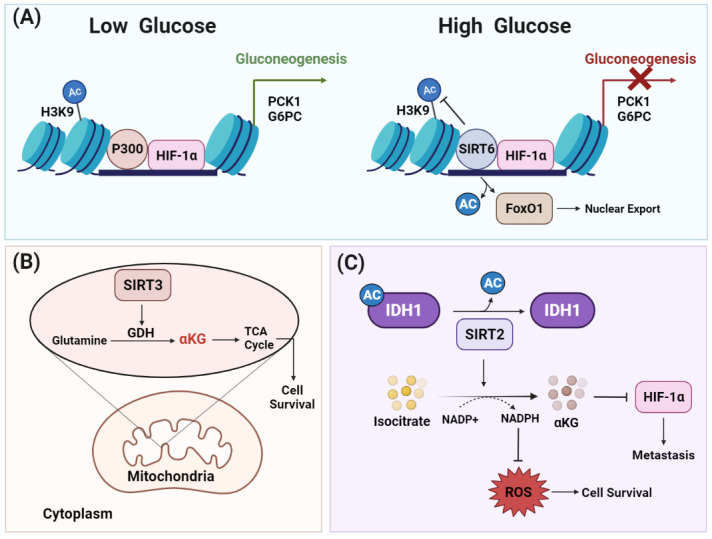
HDACs elicit metabolic reprogramming to support cell survival under metabolic stress. Different HDACs are involved in reglueing several metabolic pathways. (A) Under low glucose levels, histone acetyltransferase p300 acts as coactivator for HIF-1α to induce transcription of genes involved in gluconeogenesis. Under high glucose levels, SIRT6 inhibits gluconeogenesis by acting as a co-repressor of HIF-1α transcriptional activity by deacetylating H3K9 at the promoter sites of its target glycolytic genes such as PCK1 and G6PC, which are a rate-limiting enzymes in glucose synthesis. SIRT6 deacetylates the transcription factor FoxO1, which results in its export to the cytoplasm. Excluding FoxO1 from the nucleus reduces the expression of PCK1 and G6PCm thereby inhibiting gluconeogenesis. (B) The mitochondrial lysine deacetylase SIRT3 promotes glutamine flux to the TCA cycle via glutamate dehydrogenase, which, in turn, shields the cancer cells from metabolic stress and maintains cell survival. (C) SIRT2 deacetylates IDH1 at lysine 224 and stimulates its metabolic activity. IDH catalyzes the decarboxylation of isocitrate to produce alpha-ketoglutarate (αKG), which is important for the hydroxylation and degradation of HIF-1α. Consequently, SIRT2-dependent IDH1 deacetylation inhibits metastasis as well as decreasing reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels by producing NADPH, an ultimate donor for ROS-detoxifying enzymes. Abbreviations: HIF-1α, hypoxia-inducible factor-1; FoxO1, Forkhead box protein O1; PCK1, phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase 1; G6PC, glucose-6-phosphatase catalytic subunit; IDH1, isocitrate dehydrogenase 1; αKG, alpha-ketoglutarate; ROS, reactive oxygen species; GDH, glutamate dehydrogenase; TCA, tricarboxylic acid.
