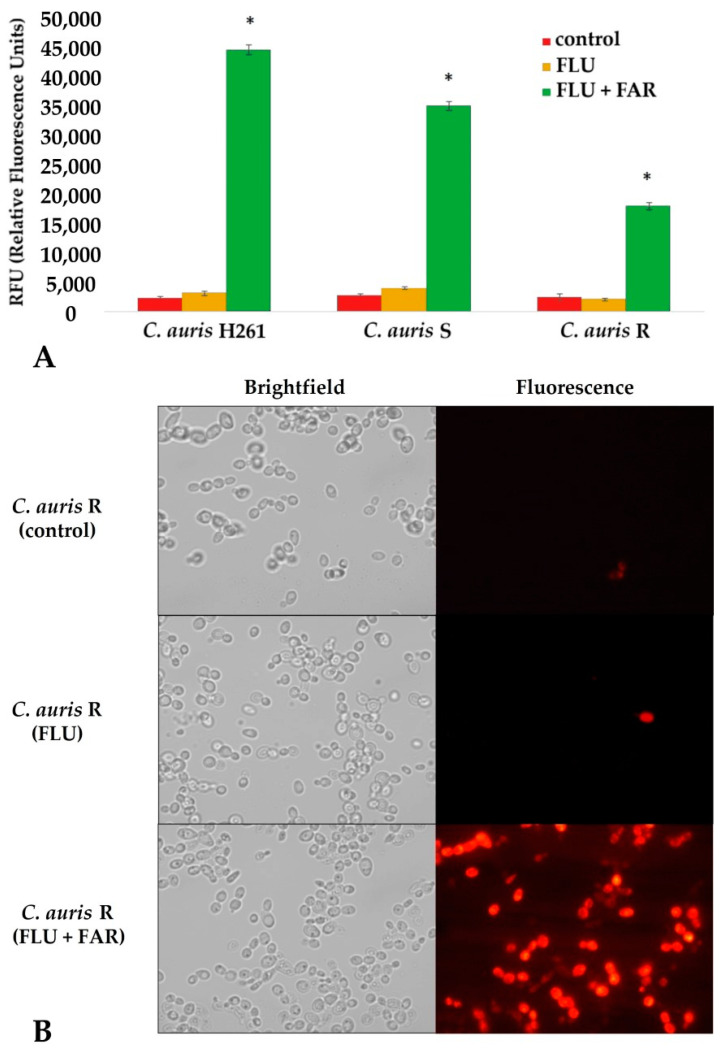
Figure 5.
(A) Rhodamine 6G intracellular accumulation measured by relative fluorescence. The figure shows a significant increase in the accumulation of R6G dye in all C. auris treated with a combination of FAR and FLU resulting in the highest abundance of fluorescence (green columns). The cells treated only with the subinhibitory concentration of FLU (yellow columns) have the same level of R6G as control cells without any agent (red columns) which means that R6G was extruded from cells by efflux. Subinhibitory concentrations of FLU were as follows: 0.06 μg/mL for C. auris H261, 8 μg/mL for C. auris S, and 32 μg/mL for C. auris R. (B) Fluorescence microscopy of the selected yeast suspension of the most resistant isolate C. auris R confirms the highest accumulation of R6G in the cells after a combination of FAR and FLU, confirming FAR as an inhibitor of efflux pump Cdr1; p-values * < 0.05 were considered significant.