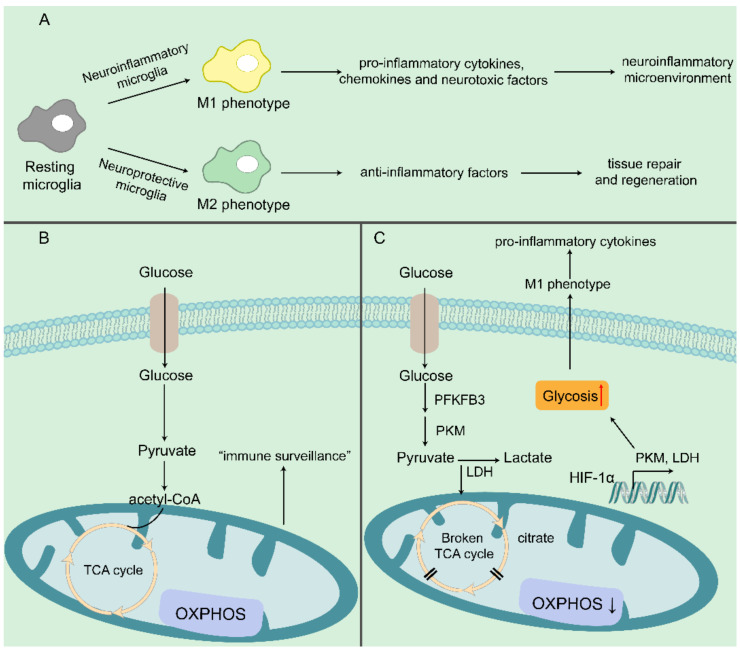
Figure 2.
The role of microglia in neuroinflammation. (A) In a dichotomy model, the M1-type microglia typically express pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines and neurotoxic factors, while the M2-type microglia generally produce anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective and wound-healing factors. (B) In the healthy brain, microglia are metabolically flexible and can use glucose to support homeostatic “immune surveillance” functions. (C) Under pathological conditions, such as AD, microglia display a metabolic reprogramming featured by broken TCA cycle. HIF1α, hypoxia inducible factor-1α; PKM, Pyruvate kinase isozyme typeM2; PFKFB3, phosphofructokinase-2/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase 3; OXPHOS, Oxidative phosphorylation; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase. Brown rectangle: glucose transporter; yellow cycle: TCA cycle; purple rectangle: oxidative phosphorylation; orange rectangle: increased glycolysis.