Figure 1. Simplified diagnostic flow of cardiac sarcoidosis using 2016 Japanese Circulation Society guidelines.
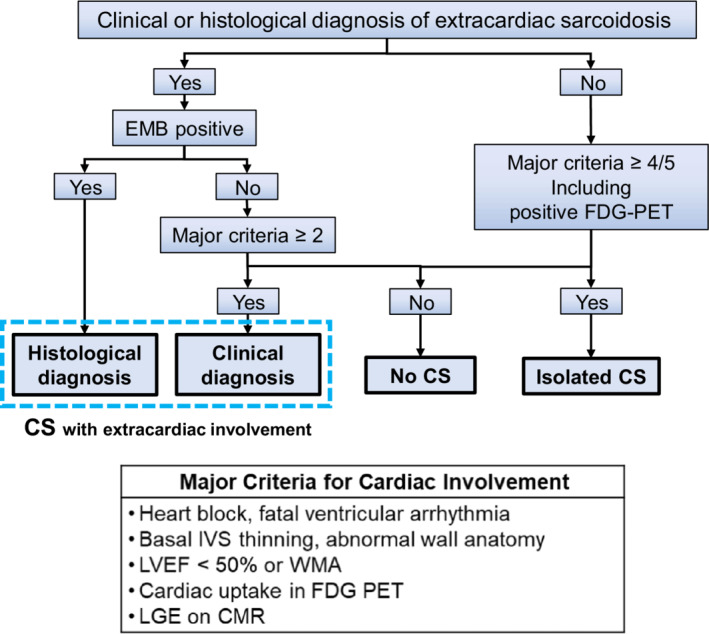
Patients were classified as having CS with extracardiac involvement, isolated CS, or no CS. In patients with evidence of a clinical or histological diagnosis of extracardiac sarcoidosis, when an endomyocardial biopsy revealed noncaseating epithelioid granulomas, patients were histologically diagnosed with CS. If CS was not confirmed on endomyocardial biopsy, the presence of major criteria for cardiac involvement was investigated. Patients meeting ≥2/5 major criteria were clinically diagnosed with CS. In patients with no evidence of extracardiac involvement, patients were diagnosed with isolated CS if they had FDG‐PET uptake and ≥3 positive major criteria other than FDG‐PET findings. CMR indicates cardiac magnetic resonance imaging; CS, cardiac sarcoidosis; EMB, endomyocardial biopsy; FDG‐PET, 18F‐fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography; IVS, interventricular septum; LVEF, left ventricular ejection fraction; LGE, late gadolinium enhancement; and WMA, wall motion abnormality.
