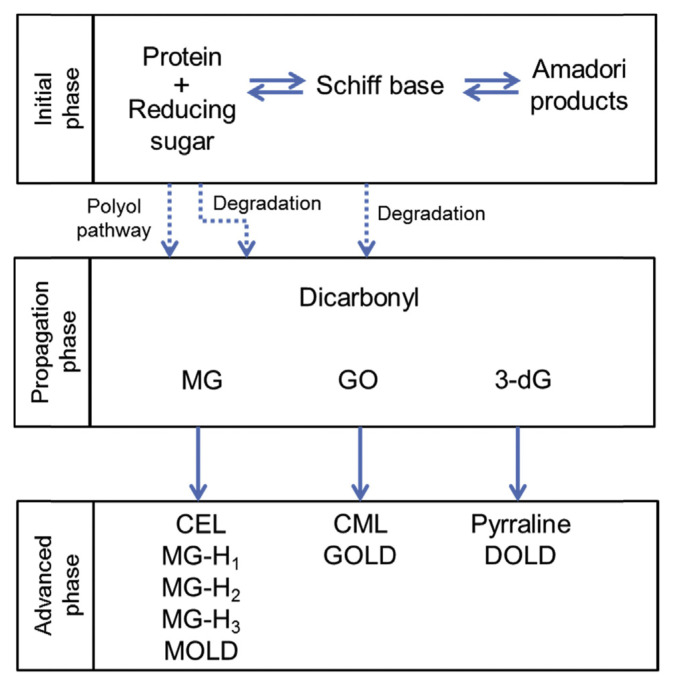
Figure 1.
Pathway for AGE formation. The N-terminal amino groups of protein and reducing sugar form dicarbonyls including methylglyoxal, glyoxal, and 3-deoxyglucosone through polyol pathway, glycolysis, or autoxidation of reducing sugar, leading to generation of pathological AGEs. AGE=advanced glycation end product; CEL=N ɛ-carboxyethyllysine; CML=N ɛ-carboxymethyllysine; 3-dG=3-deoxyglucosone; DOLD=3-deoxyglucosone lysine dimer; GO=glyoxal; GOLD=glyoxal-lysine dimer; MG=methylglyoxal; MGH =MG-derived-hydroimidazalone; MOLD=methylglyoxal-lysine dimer.