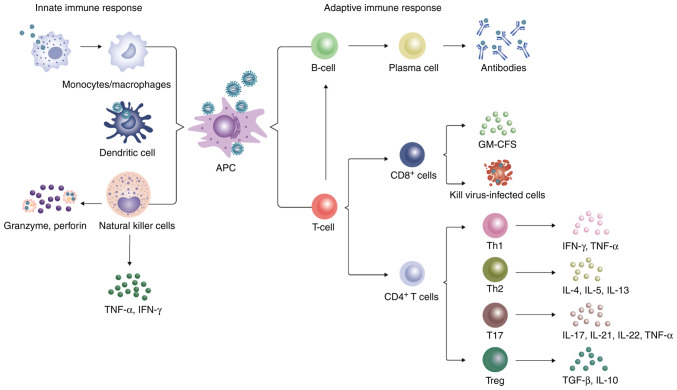
Figure 2.
Innate immune response and the adaptive immune response against SFTSV. The antigen is presented to adaptive immune cells after recognizing the SFTSV by monocytes/macrophages, dendritic cells and NK cells. In addition, monocytes/macrophages can engulf the virus to induce apoptosis, whereas NK cells can release perforin and granzyme to lyse lean virus-infected cells. CD8+ T cells can directly kill virus-infected cells by removing cytotoxic particles. Naïve CD4+ T cells can differentiate into Th1, Th2, Th17 and Tregs under different cytokine environments. These helper T cells secrete various cytokines that provoke an inflammatory storm, leading to harmful outcomes and possibly to lymphopenia. T cells recognize virus-antigens presented by major histocompartibility complex II and stimulate the proliferation and differentiation of B cells by secreting cytokines. A portion of B cells differentiates into Ig-secreting plasma cells, which secrete anti-SFTSV antibodies. SFTSV, severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus; NK, natural killer.