Figure 2. ZBP1 requires Zα2 to sense VACV and trigger necroptosis.
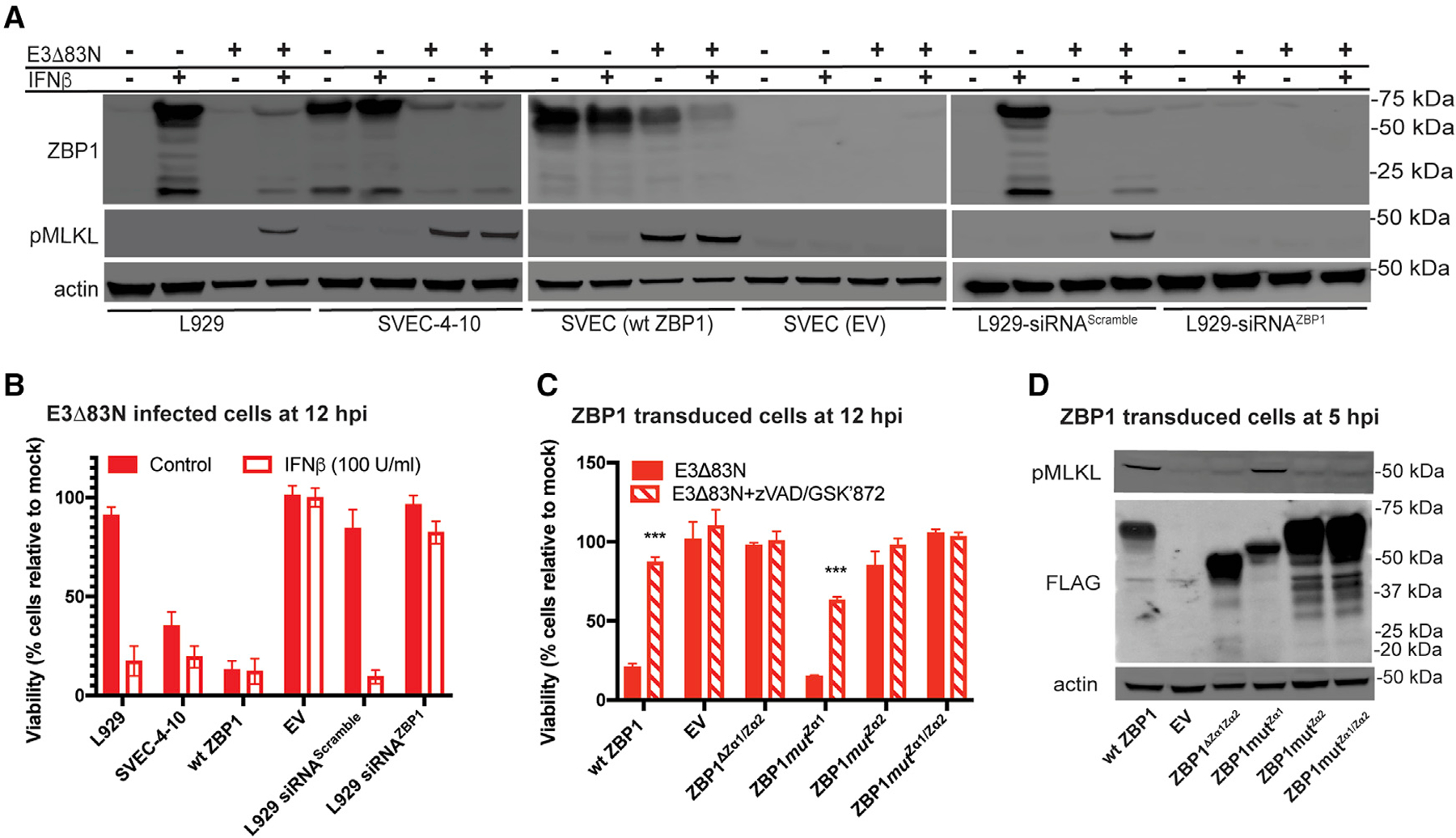
(A) IB of L929, SVEC4–10, FLAG-ZBP1-reconstituted SVEC (WT ZBP1) and ZBP1-null SVEC (EV) (Sridharan et al., 2017) cells either left untreated (−) or pretreated with 100 U/mL of mouse IFN-β for 18 h (+) and either left uninfected (−) or infected at an MOI of 5 with E3Δ83N (+). L929 cells in rightmost panel were transfected with either a scrambled siRNA pool or an siRNA pool targeting ZBP1 for 36 h prior to IFN-β treatment. Lysates were harvested at 4 hpi, and, following SDS-PAGE, evaluated for phospho-MLKL and ZBP1.
(B) Viability of L929, SVEC4–10, WT ZBP1 or EV cells either untreated or pretreated with IFN-β and then infected at an MOI of 5 with E3Δ83N for 12 h determined by measuring intracellular ATP levels with a Cell Titer-Glo luminescent cell viability assay kit. Rightmost bars show results from cells transfected with either a scrambled siRNA pool or an siRNA pool targeting ZBP1 as described in (A). CellTiter-Glo assay (Promega).
(C) Viability of ZBP1-null SVEC29–11 cells reconstituted with indicated ZBP1 constructs infected with E3Δ83N either alone or in combination with zVAD-fmk plus GSKʹ872 assessed at 12 hpi by CellTiter-Glo assay as described in (B).
(D) IB of ZBP1-reconstituted SVEC29–11 cells infected at a MOI of 5. Lysates were prepared as described in (A) and evaluated for phospho-MLKL and FLAG-ZBP1.
Error bars represent the SD. Each set of data is representative of two replicates except for (B) and (C), which compiles the results of the replicates. Statistical significance was determined as described in Figure 1.
