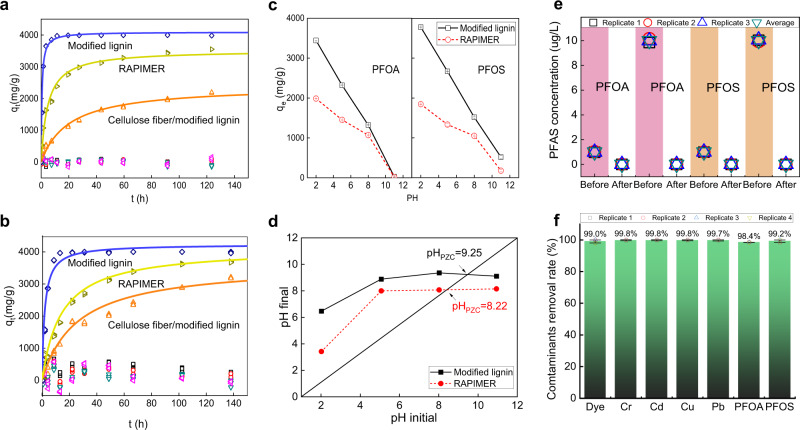
Fig. 3. The characterization of material/PFAS adsorption.
a The PFOA adsorption kinetics of the bioinspired composite and their components. b The PFOS adsorption kinetics of the bioinspired composite and their components. Blue diamond and curve: modified lignin, yellow-green triangle and curve: RAPIMER, orange triangle and curve: cellulose fiber/modified lignin composite, green triangle: cellulose nanofibrils, purple triangle: cellulose nanofibril/lignin composite, green square: cellulose fibers. Each time points are triplicate measurements. Due to the small variations, some replicates are overlapped and all points are shown in the figures (the invisible standard derivations are not applied in the figure due to the small variations). c pH dependence of the modified lignin and RAPIMER composite adsorption capacity. Red open circle, RAPIMER composite; black open square, modified lignin. d pH of zero charge of the modified lignin and RAPIMER composite. Red solid circle, RAPIMER composite; black solid square, modified lignin. e Adsorption efficiency of the RAPIMER composites for PFOA and PFOS at 1 and 10 µg/L. The peristaltic pump filtration system was employed for this PFAS adsorption measurements (Supplementary Fig. S8). The experiment was reproduced n = 3 times. f Adsorption efficiency of the RAPIMER composites for 1 mg/L PFOS, PFOA, anionic dye, chromium (Cr), cadmium (Cd), copper (Cu), lead (Pb) mixtures in the rain water. The peristaltic pump filtration system was employed for this PFAS adsorption measurements (Supplementary Fig. S8). The mean with error bar represents the average value and standard deviation (SD) of experimental replicates. The experiment was reproduced n = 4 times (The ICP-MS measurement was reproduced twice due to the high precision). The Source data is provided as a Source Data file.