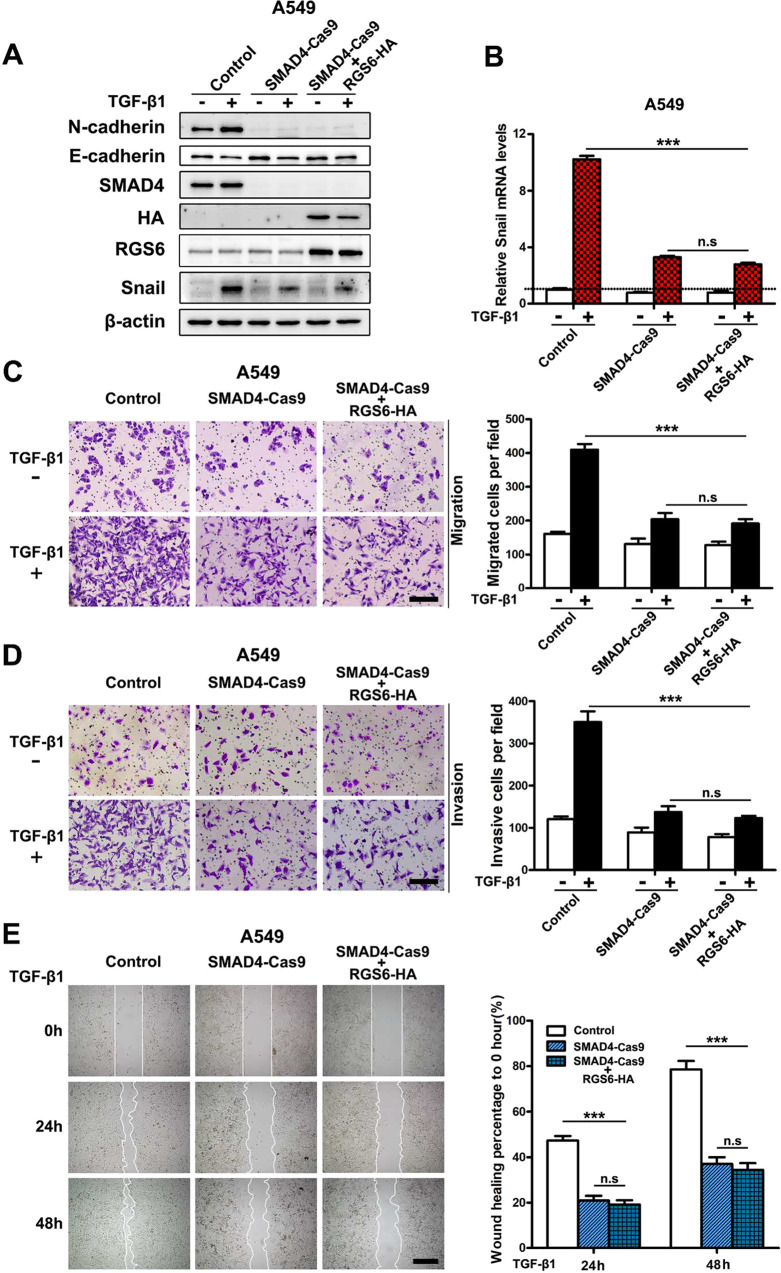
Fig. 6. RGS6 suppresses TGF-β-induced pro-EMT signaling and EMT events via a SMAD4-dependent mechanism.
We examined the effect of RGS6 overexpression on TGF-β-induced pro-EMT signaling and EMT events in SMAD4-KD cells. If RGS6 can act through a mechanism not involving SMAD4 to suppress TGF-β-induced EMT, overexpressing RGS6 should cause a greater inhibition on TGF-β-induced EMT in SMAD4-KD cells. A SMAD4-Cas9 cells were transfected with RGS6 or control vector. Cells were then treated with or without TGF-β (5 ng/ml) for 24 h. Cell lysates were collected and subjected to immunoblotting for indicated proteins. B SMAD4-Cas9 cells were transfected with RGS6 or control vector. Cells were then treated with or without TGF-β (5 ng/ml) for 2 h and subjected to qRT-PCR for detection of Snail mRNA level (***p < 0.001). C, D SMAD4-Cas9 cells were transfected with RGS6 or control vector and subjected to migration assay (C) and invasion assay (D). Left, representative images. Right, quantification of cell migration (C) and cell invasion (D). Scale bar, 100 μm (***p < 0.001). E SMAD4-Cas9 cells were transfected with RGS6 or control vector and subjected to wound-healing assay. Left, representative images. Right, quantification of rate of wound healting. Scale bar, 200 μm (***p < 0.001).