Fig. 5.
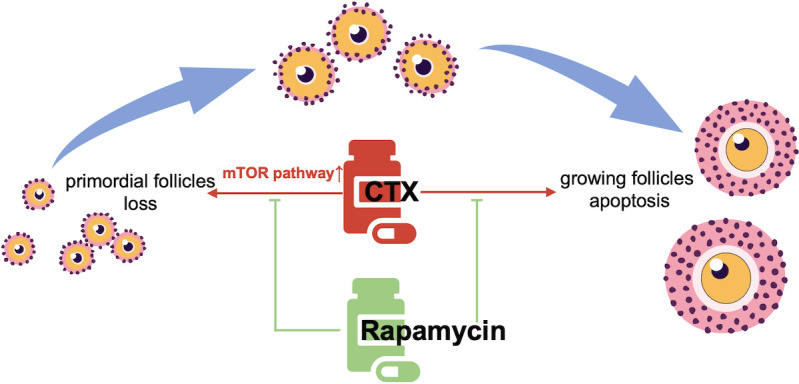
Illustrative diagram showing the protective function of rapamycin on CTX-induced ovarian reserve injury. CTX exposure causes loss of primordial follicles and apoptosis in developing follicles via activation of the mTOR signaling pathway. Rapamycin intervention alleviates the overactivation of the mTOR signaling pathway, thereby protecting the primordial follicle pool and reducing apoptosis of developing follicles. CTX, cyclophosphamide.
