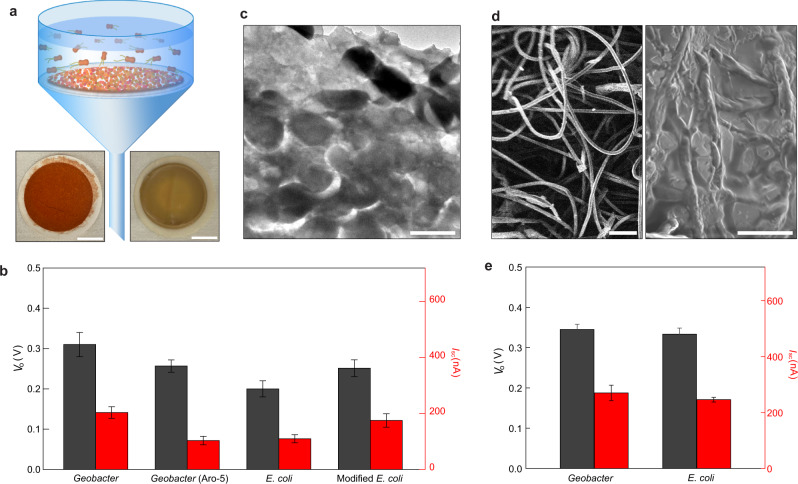
Fig. 4. Devices made from filtered biofilm-mats.
a Schematic of harvesting biofilm-mats by filtering microbial solutions. The bottom photos show filtered (left) G. sulfurrenducens and (right) E. coli mats, respectively. Scale bars, 1 cm. b Average Vo (gray) and Isc (red) measured from devices fabricated with biofilm-mats of G. sulfurreducens, genetically modified G. sulfurrenducens Aro-5 strain, E. coli, and genetically modified E. coli strain. The devices had the same size of 5 × 5 mm2, with a porosity of 0.4 and pore size of 100 µm in the mesh electrodes. c Cross-sectional TEM image of a biofilm-mat assembled by filtered E. coli. Scale bar, 1 µm. d Scanning electron microscope images of (left) a tissue paper and (right) a tissue paper infiltrated with E. coli. Scale bars, (left) 100 µm, (right) 10 µm. e Average Vo (gray) and Isc (red) measured from devices fabricated with tissue paper infiltrated with Geobacter and E. coli. The devices had the same size of 5 × 5 mm2, with a porosity of 0.4 and pore size of 100 µm in the mesh electrodes. All the error bars are standard deviations.