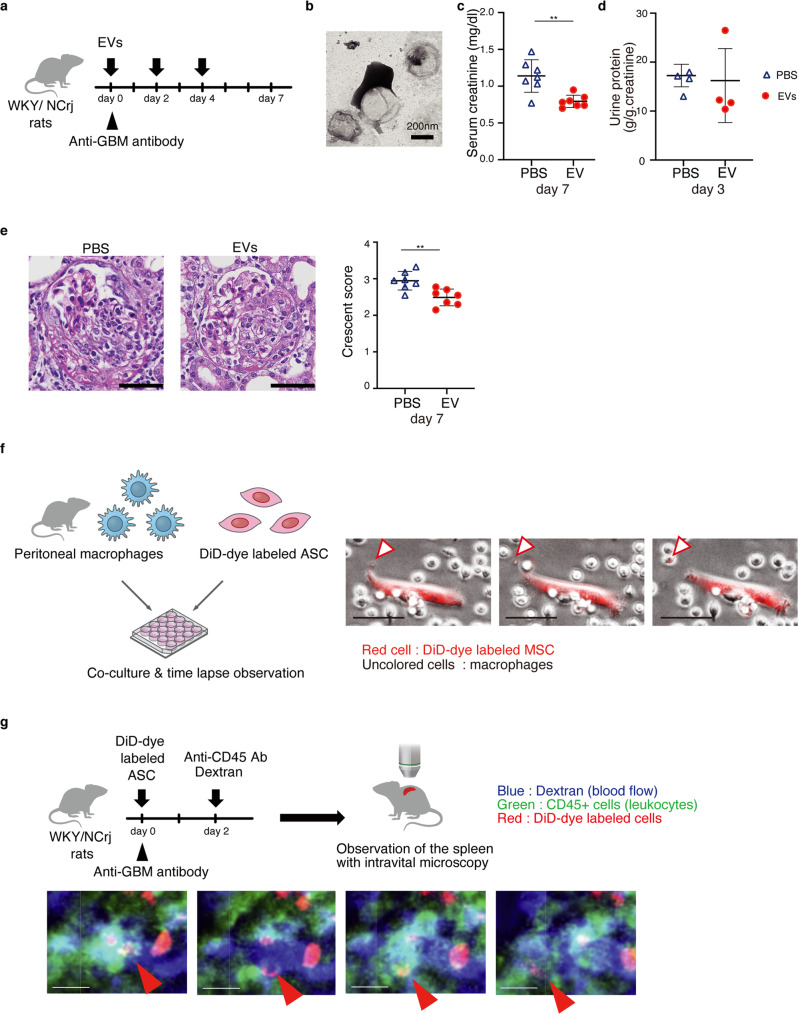
Fig. 7. EVs have therapeutic potential for anti-glomerular nephritis.
a Experimental scheme to determine therapeutic potentials of EVs for anti-GBM nephritis. EVs were administered intravenously on days 0, 2, and 4. b Electron micrograph of EVs. c The serum creatinine level on day 7 after EV treatment (n = 7 per group). d The urine protein excretion on day 3 (n = 4 per group). e Representative images of kidney sections stained with Periodic Acid-Schiff on day 7. Scale bars, 50 μm. The glomerular injury was evaluated using crescent score (n = 7 per group). f Experimental scheme of the co-culture of peritoneal macrophage and DiD-dye labeled ASCs. Time-lapse imaging show that EVs generated from the DiD-dye labeled ASCs are captured by macrophages. Scale bars, 50 μm. g Experimental scheme for observing dynamics of EV-transferred leukocytes using intravital microscopy. Time-lapse imaging of the spleen shows that the DiD+ leukocytes move into the bloodstream. Scale bars, 10 μm. **p ≤ 0.01 as determined by Welch’s t-test.