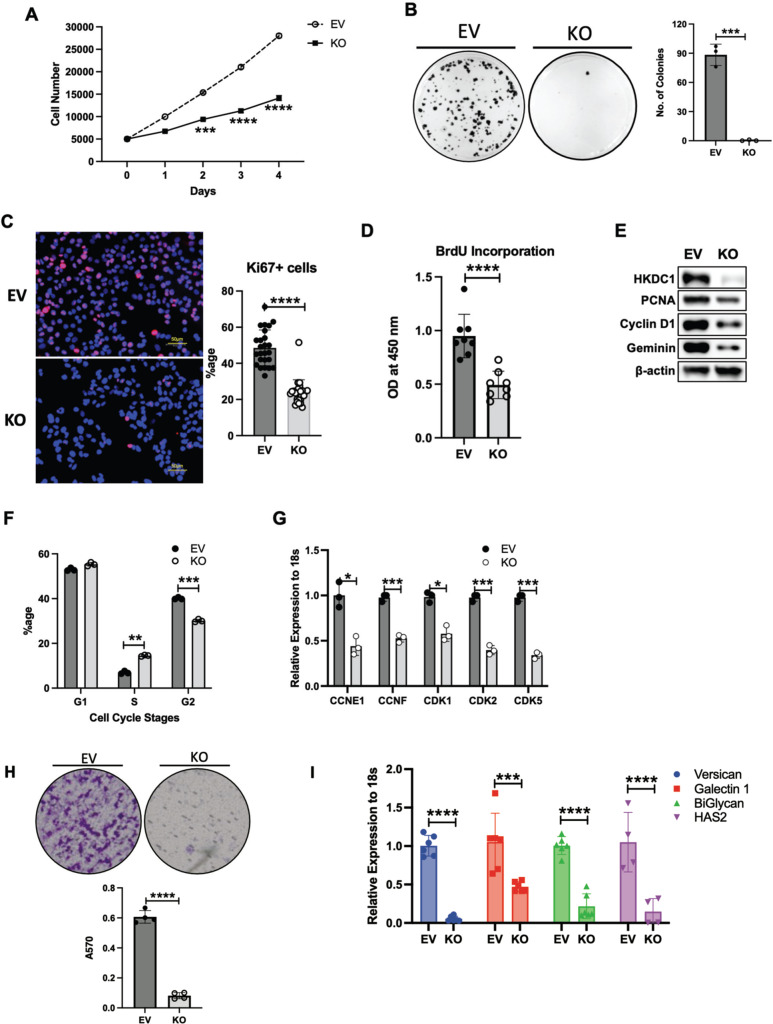
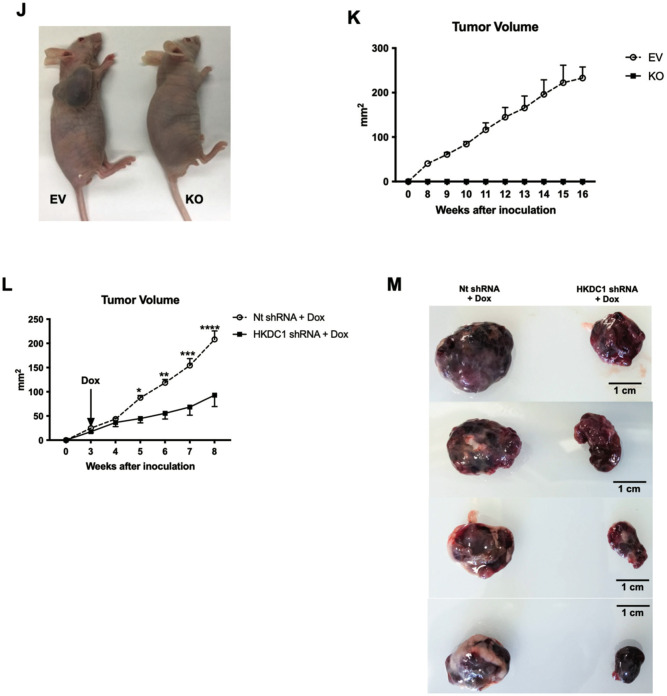
Fig. 2. HKDC1 is essential for LC progression and survival.
EV and HKDC1-KO cells (KO) were used for A cell proliferation assay, B colony-forming assay (left panel images representative of three images per group and right panel number of colonies were counted using Image J), C immunostaining for Ki67 proliferative marker (pink), nuclei are stained with DAPI (blue), D Cell proliferation was measured using the BrdU assay, E Western blot analysis was done in EV and KO cells for markers of cell proliferation and cell cycle (representative of two independent blots). F Cell-cycle analysis with propidium iodide, G mRNA expression by qPCR for cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases. H In invasion assay, EV and KO cell suspensions (2 × 105 cells/well) were added to the upper chambers and allowed to invade for 72 h. Invasive cells were stained with 0.1% crystal violet (upper panel) and were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay reader using 570 nm as test wavelength (lower panel). I mRNA expression by qPCR for proteoglycan synthesis genes. J In vivo tumor growth was assessed where 1 × 106 EV or KO cells were inoculated into 4–6-week-old male Nu/J mice (n = 5), images were taken at endpoint (16 weeks post inoculation). K Tumor size was measured weekly till 16 weeks after appearance of tumor with a vernier caliper tumor weight till the end of the study. L Hep3B2 cells were transfected with shHKDC1 or (non-target) ntshRNA and transfected cells were selected with appropriate antibiotics, 1 × 106 cells were inoculated into mice (n = 4). When tumors were visible, mice were given doxycycline (in diet) for 7 days to activate shRNAs. Tumor growth was measured weekly till 8 weeks after appearance of tumor with a vernier caliper. M Images of tumors at endpoint. All cell-line experiments (A–G) were performed 2–3 times with 3–5 replicates per experiment. Values are mean ± SD; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001 by Student’s t-test, or two-way ANOVA (for K).