Fig. 6. Primary cilium loss induced by palmitic acid or autophagy impairment reduces insulin sensitivity.
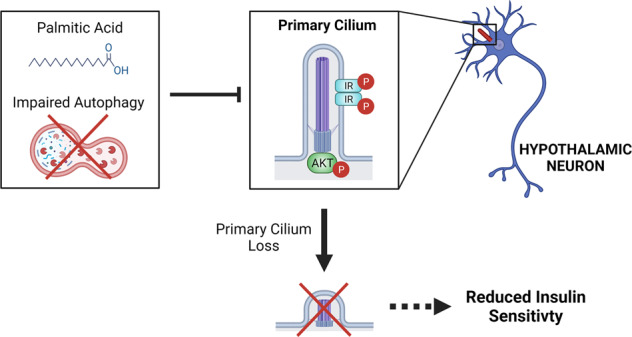
Our results indicate that conditions which impair autophagy, such as PA exposure or chemical and genetic inhibition of autophagy, obtained by treatment with the autophagy inhibitor Bafilomycin A1 or Chloroquine or downregulation of essential autophagy genes, causes cilia loss in hypothalamic neuronal cells. We also show that proteins required for insulin signaling (IR and AKT) localize at the primary cilium, promoting insulin sensitivity. Consistently, conditions that cause cilia loss impair insulin signaling in hypothalamic neurons. p-IR: phosphorylated insulin receptor; p-AKT: phosphorylated protein kinase B (also known as AKT). Figure created with BioRender.com.
