Figure 1.
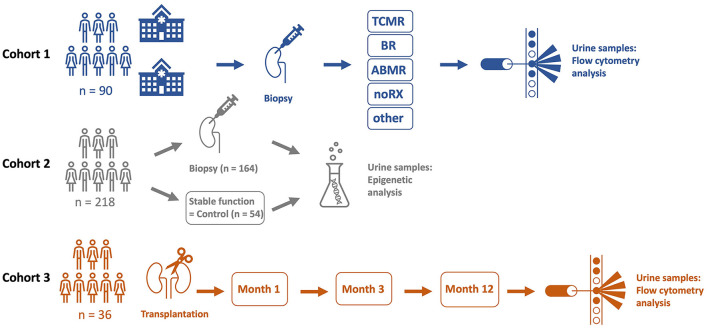
A total of three different cohorts were analyzed in this trial. Cohort 1 included 90 kidney transplant (KT) patients from two hospitals (Charité University Hospital, Berlin, Germany and Carl Gustav Carus University Hospital, Dresden, Germany) who underwent kidney biopsy due to graft deterioration. Patients were categorized by histopathological diagnosis and urine samples were analyzed by flow cytometry. In cohort 2, urine samples of 218 KT patients were subject to epigenetic qPCR analysis. 164 patients of cohort 2 underwent kidney biopsy because of graft deterioration, 54 stable KT patients served as a control group. Cohort 3 included 36 KT patients. Urine samples were analyzed on three scheduled visits by flow cytometry in a follow-up setting during the first year after transplantation.